B-Spline Basis Functions
eryar@163.com
摘要Abstract:直接根据B样条的Cox-deBoor递推定义写出计算B样条基函数的程序,并将计算结果在OpenSceneGraph中显示。
关键字Key Words:B Spline Basis Functions、OpenSceneGraph
一、概述Overview
有很多方法可以用来定义B样条基函数以及证明它的一些重要性质。例如,可以采用截尾幂函数的差商定义,开花定义,以及由de Boor和Cox等人提出的递推公式等来定义。我们这里采用的是递推定义方法,因为这种方法在计算机实现中是最有效的。
令U={u0,u1,…,um}是一个单调不减的实数序列,即ui<=ui+1,i=0,1,…,m-1。其中,ui称为节点,U称为节点矢量,用Ni,p(u)表示第i个p次B样条基函数,其定义为:
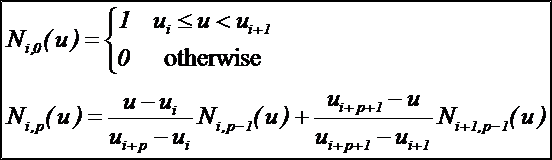
B样条基有如下性质:
a) 递推性;
b) 局部支承性;
c) 规范性;
d) 可微性;
二、程序 Codes
直接根据B样条基函数的Cox-deBoor递推定义,写出计算B样条基函数的程序如下:
头文件BSplineBasisFunction.h:

 /**//*
/**//*
 * Copyright (c) 2013 eryar All Rights Reserved.
* Copyright (c) 2013 eryar All Rights Reserved.
 *
*
 * File : BSplineBasisFunction.h
* File : BSplineBasisFunction.h
 * Author : eryar@163.com
* Author : eryar@163.com
 * Date : 2013-03-23 22:13
* Date : 2013-03-23 22:13
 * Version : V1.0
* Version : V1.0
 *
*
 * Description : Use Cox-deBoor formula to implemente the
* Description : Use Cox-deBoor formula to implemente the
 * B-Spline Basis functions.
* B-Spline Basis functions.
 *
*
 */
*/
 #ifndef _BSPLINEBASISFUNCTION_H_
#ifndef _BSPLINEBASISFUNCTION_H_
 #define _BSPLINEBASISFUNCTION_H_
#define _BSPLINEBASISFUNCTION_H_

 #include <vector>
#include <vector>

 class BSplineBasisFunction
class BSplineBasisFunction


 {
{
 public:
public:
 BSplineBasisFunction(const std::vector<double>& U);
BSplineBasisFunction(const std::vector<double>& U);
 ~BSplineBasisFunction(void);
~BSplineBasisFunction(void);

 public:
public:

 /**//*
/**//*
 * @brief Binary search of the knot vector.
* @brief Binary search of the knot vector.
 */
*/
 int FindSpan(double u);
int FindSpan(double u);


 /**//*
/**//*
 * @brief
* @brief
 * @param [in] i: span of the parameter u;
* @param [in] i: span of the parameter u;
 * [in] p: degree;
* [in] p: degree;
 * [in] u: parameter;
* [in] u: parameter;
 */
*/
 double EvalBasis(int i, int p, double u);
double EvalBasis(int i, int p, double u);


 /**//*
/**//*
 * @breif Get knot vector size.
* @breif Get knot vector size.
 */
*/
 int GetKnotVectorSize(void) const;
int GetKnotVectorSize(void) const;


 /**//*
/**//*
 * @breif Get the knot value of the given index.
* @breif Get the knot value of the given index.
 */
*/
 double GetKnot(int i) const;
double GetKnot(int i) const;

 private:
private:
 std::vector<double> mKnotVector;
std::vector<double> mKnotVector;
 };
};

 #endif // _BSPLINEBASISFUNCTION_H_
#endif // _BSPLINEBASISFUNCTION_H_



实现文件BSplineBasisFunction.cpp:

 /**//*
/**//*
 * Copyright (c) 2013 eryar All Rights Reserved.
* Copyright (c) 2013 eryar All Rights Reserved.
 *
*
 * File : BSplineBasisFunction.cpp
* File : BSplineBasisFunction.cpp
 * Author : eryar@163.com
* Author : eryar@163.com
 * Date : 2013-03-23 22:14
* Date : 2013-03-23 22:14
 * Version : V1.0
* Version : V1.0
 *
*
 * Description : Use Cox-deBoor formula to implemente the
* Description : Use Cox-deBoor formula to implemente the
 * B-Spline Basis functions.
* B-Spline Basis functions.
 *
*
 */
*/

 #include "BSplineBasisFunction.h"
#include "BSplineBasisFunction.h"

 BSplineBasisFunction::BSplineBasisFunction( const std::vector<double>& U )
BSplineBasisFunction::BSplineBasisFunction( const std::vector<double>& U )
 :mKnotVector(U)
:mKnotVector(U)


 {
{

 }
}


 BSplineBasisFunction::~BSplineBasisFunction(void)
BSplineBasisFunction::~BSplineBasisFunction(void)


 {
{
 }
}

 int BSplineBasisFunction::GetKnotVectorSize( void ) const
int BSplineBasisFunction::GetKnotVectorSize( void ) const


 {
{
 return static_cast<int> (mKnotVector.size());
return static_cast<int> (mKnotVector.size());
 }
}

 double BSplineBasisFunction::GetKnot( int i ) const
double BSplineBasisFunction::GetKnot( int i ) const


 {
{
 return mKnotVector[i];
return mKnotVector[i];
 }
}


 /**//*
/**//*
 * @brief Binary search of the knot vector.
* @brief Binary search of the knot vector.
 */
*/
 int BSplineBasisFunction::FindSpan( double u )
int BSplineBasisFunction::FindSpan( double u )


 {
{
 int iSize = static_cast<int> (mKnotVector.size());
int iSize = static_cast<int> (mKnotVector.size());

 if (u >= mKnotVector[iSize-1])
if (u >= mKnotVector[iSize-1])


 {
{
 return iSize;
return iSize;
 }
}

 int iLow = 0;
int iLow = 0;
 int iHigh = iSize;
int iHigh = iSize;
 int iMiddle = (iLow + iHigh) / 2;
int iMiddle = (iLow + iHigh) / 2;

 while (u < mKnotVector[iMiddle] || u > mKnotVector[iMiddle+1])
while (u < mKnotVector[iMiddle] || u > mKnotVector[iMiddle+1])


 {
{
 if (u < mKnotVector[iMiddle])
if (u < mKnotVector[iMiddle])


 {
{
 iHigh = iMiddle;
iHigh = iMiddle;
 }
}
 else
else


 {
{
 iLow = iMiddle;
iLow = iMiddle;
 }
}

 iMiddle = (iLow + iHigh) / 2;
iMiddle = (iLow + iHigh) / 2;
 }
}

 return iMiddle;
return iMiddle;
 }
}

 double BSplineBasisFunction::EvalBasis( int i, int p, double u )
double BSplineBasisFunction::EvalBasis( int i, int p, double u )


 {
{
 if ((i+p+1) >= GetKnotVectorSize())
if ((i+p+1) >= GetKnotVectorSize())


 {
{
 return 0;
return 0;
 }
}

 if (0 == p)
if (0 == p)


 {
{
 if (u >= mKnotVector[i] && u < mKnotVector[i+1])
if (u >= mKnotVector[i] && u < mKnotVector[i+1])


 {
{
 return 1;
return 1;
 }
}
 else
else


 {
{
 return 0;
return 0;
 }
}
 }
}

 double dLeftUpper = u - mKnotVector[i];
double dLeftUpper = u - mKnotVector[i];
 double dLeftLower = mKnotVector[i+p] - mKnotVector[i];
double dLeftLower = mKnotVector[i+p] - mKnotVector[i];
 double dLeftValue = 0;
double dLeftValue = 0;

 double dRightUpper = mKnotVector[i+p+1] - u;
double dRightUpper = mKnotVector[i+p+1] - u;
 double dRightLower = mKnotVector[i+p+1] - mKnotVector[i+1];
double dRightLower = mKnotVector[i+p+1] - mKnotVector[i+1];
 double dRightValue = 0;
double dRightValue = 0;

 if (dLeftUpper != 0 && dLeftLower != 0)
if (dLeftUpper != 0 && dLeftLower != 0)


 {
{
 dLeftValue = (dLeftUpper / dLeftLower) * EvalBasis(i, p-1, u);
dLeftValue = (dLeftUpper / dLeftLower) * EvalBasis(i, p-1, u);
 }
}

 if (dRightUpper != 0 && dRightLower != 0)
if (dRightUpper != 0 && dRightLower != 0)


 {
{
 dRightValue = (dRightUpper / dRightLower) * EvalBasis(i+1, p-1, u);
dRightValue = (dRightUpper / dRightLower) * EvalBasis(i+1, p-1, u);
 }
}

 return (dLeftValue + dRightValue);
return (dLeftValue + dRightValue);
 }
}

主函数:

 /**//*
/**//*
 * Copyright (c) 2013 eryar All Rights Reserved.
* Copyright (c) 2013 eryar All Rights Reserved.
 *
*
 * File : Main.cpp
* File : Main.cpp
 * Author : eryar@163.com
* Author : eryar@163.com
 * Date : 2013-03-23 22:11
* Date : 2013-03-23 22:11
 * Version : V1.0
* Version : V1.0
 *
*
 * Description : Use Cox-deBoor formula to implemente the
* Description : Use Cox-deBoor formula to implemente the
 * B-Spline Basis functions.
* B-Spline Basis functions.
 *
*
 */
*/

 #include <osgDB/ReadFile>
#include <osgDB/ReadFile>
 #include <osgViewer/Viewer>
#include <osgViewer/Viewer>
 #include <osgGA/StateSetManipulator>
#include <osgGA/StateSetManipulator>
 #include <osgViewer/ViewerEventHandlers>
#include <osgViewer/ViewerEventHandlers>

 #include "BSplineBasisFunction.h"
#include "BSplineBasisFunction.h"

 #pragma comment(lib, "osgd.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "osgd.lib")
 #pragma comment(lib, "osgDBd.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "osgDBd.lib")
 #pragma comment(lib, "osgGAd.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "osgGAd.lib")
 #pragma comment(lib, "osgViewerd.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "osgViewerd.lib")

 osg::Node* MakeBasisFuncLine(BSplineBasisFunction& bf, int i, int p)
osg::Node* MakeBasisFuncLine(BSplineBasisFunction& bf, int i, int p)


 {
{
 // The property basis functions.
// The property basis functions.
 int iLen = bf.GetKnotVectorSize();
int iLen = bf.GetKnotVectorSize();
 int iStep = 800;
int iStep = 800;
 double dStart = bf.GetKnot(0);
double dStart = bf.GetKnot(0);
 double dEnd = bf.GetKnot(iLen-1);
double dEnd = bf.GetKnot(iLen-1);
 double dDelta = (dEnd - dStart) / iStep;
double dDelta = (dEnd - dStart) / iStep;
 double u = 0;
double u = 0;
 double v = 0;
double v = 0;

 // Create the Geode (Geometry Node) to contain all our osg::Geometry objects.
// Create the Geode (Geometry Node) to contain all our osg::Geometry objects.
 osg::Geode* geode = new osg::Geode;
osg::Geode* geode = new osg::Geode;

 // Create Geometry object to store all the vertices and lines primitive.
// Create Geometry object to store all the vertices and lines primitive.
 osg::ref_ptr<osg::Geometry> linesGeom = new osg::Geometry;
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Geometry> linesGeom = new osg::Geometry;

 // Set the vertex array to the points geometry object.
// Set the vertex array to the points geometry object.
 osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec3Array> pointsVec = new osg::Vec3Array;
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec3Array> pointsVec = new osg::Vec3Array;

 for (int s = 0; s <= iStep; s++)
for (int s = 0; s <= iStep; s++)


 {
{
 u = s * dDelta;
u = s * dDelta;
 v = bf.EvalBasis(i, p, u);
v = bf.EvalBasis(i, p, u);
 if (v != 0)
if (v != 0)


 {
{
 pointsVec->push_back(osg::Vec3(u, 0, v));
pointsVec->push_back(osg::Vec3(u, 0, v));
 }
}
 }
}
 linesGeom->setVertexArray(pointsVec);
linesGeom->setVertexArray(pointsVec);

 // Set the colors.
// Set the colors.
 osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec4Array> colors = new osg::Vec4Array;
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec4Array> colors = new osg::Vec4Array;
 colors->push_back(osg::Vec4(1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f));
colors->push_back(osg::Vec4(1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f));
 linesGeom->setColorArray(colors.get());
linesGeom->setColorArray(colors.get());
 linesGeom->setColorBinding(osg::Geometry::BIND_OVERALL);
linesGeom->setColorBinding(osg::Geometry::BIND_OVERALL);

 // Set the normal in the same way of color.
// Set the normal in the same way of color.
 osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec3Array> normals = new osg::Vec3Array;
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec3Array> normals = new osg::Vec3Array;
 normals->push_back(osg::Vec3(0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f));
normals->push_back(osg::Vec3(0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f));
 linesGeom->setNormalArray(normals.get());
linesGeom->setNormalArray(normals.get());
 linesGeom->setNormalBinding(osg::Geometry::BIND_OVERALL);
linesGeom->setNormalBinding(osg::Geometry::BIND_OVERALL);

 // Add the points geometry to the geode.
// Add the points geometry to the geode.
 linesGeom->addPrimitiveSet(new osg::DrawArrays(osg::PrimitiveSet::LINE_STRIP, 0, pointsVec->size()));
linesGeom->addPrimitiveSet(new osg::DrawArrays(osg::PrimitiveSet::LINE_STRIP, 0, pointsVec->size()));
 geode->addDrawable(linesGeom.get());
geode->addDrawable(linesGeom.get());

 return geode;
return geode;
 }
}

 osg::Node* CreateScene(void)
osg::Node* CreateScene(void)


 {
{
 osg::Group* root = new osg::Group;
osg::Group* root = new osg::Group;

 // Knot vector: U={0,0,0,1,2,3,4,4,5,5,5}.
// Knot vector: U={0,0,0,1,2,3,4,4,5,5,5}.
 std::vector<double> knotVector;
std::vector<double> knotVector;
 knotVector.push_back(0);
knotVector.push_back(0);
 knotVector.push_back(0);
knotVector.push_back(0);
 knotVector.push_back(0);
knotVector.push_back(0);
 knotVector.push_back(1);
knotVector.push_back(1);
 knotVector.push_back(2);
knotVector.push_back(2);
 knotVector.push_back(3);
knotVector.push_back(3);
 knotVector.push_back(4);
knotVector.push_back(4);
 knotVector.push_back(4);
knotVector.push_back(4);
 knotVector.push_back(5);
knotVector.push_back(5);
 knotVector.push_back(5);
knotVector.push_back(5);
 knotVector.push_back(5);
knotVector.push_back(5);

 BSplineBasisFunction basisFunc(knotVector);
BSplineBasisFunction basisFunc(knotVector);

 for (int i = 0; i < basisFunc.GetKnotVectorSize(); i++)
for (int i = 0; i < basisFunc.GetKnotVectorSize(); i++)


 {
{
 //
//
 //root->addChild(MakeBasisFuncLine(basisFunc, i, 1));
//root->addChild(MakeBasisFuncLine(basisFunc, i, 1));

 //
//
 root->addChild(MakeBasisFuncLine(basisFunc, i, 2));
root->addChild(MakeBasisFuncLine(basisFunc, i, 2));
 }
}

 return root;
return root;
 }
}

 int main(int argc, char* argv[])
int main(int argc, char* argv[])


 {
{
 osgViewer::Viewer viewer;
osgViewer::Viewer viewer;
 viewer.setSceneData(CreateScene());
viewer.setSceneData(CreateScene());

 viewer.addEventHandler(new osgGA::StateSetManipulator(viewer.getCamera()->getOrCreateStateSet()));
viewer.addEventHandler(new osgGA::StateSetManipulator(viewer.getCamera()->getOrCreateStateSet()));
 viewer.addEventHandler(new osgViewer::StatsHandler);
viewer.addEventHandler(new osgViewer::StatsHandler);
 viewer.addEventHandler(new osgViewer::WindowSizeHandler);
viewer.addEventHandler(new osgViewer::WindowSizeHandler);

 return viewer.run();
return viewer.run();
 }
}
若想显示出所有次数的B样条基函数,只需要在CreateScene中添加就好了。
以《The NURBS Book》中的例子2.2,节点矢量U={0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5},次数p=2,分别将程序计算的一次、二次B样条基函数的结果列出,如下图所示:
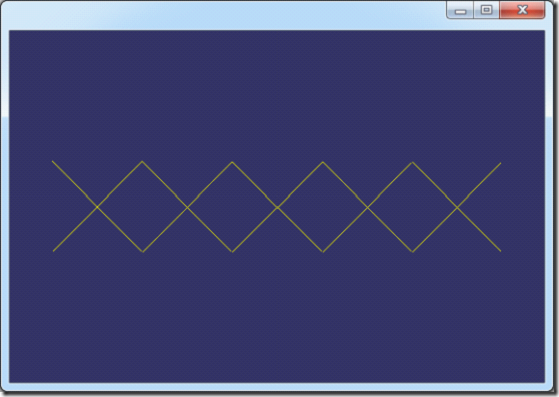
图1. 一次B样条基函数
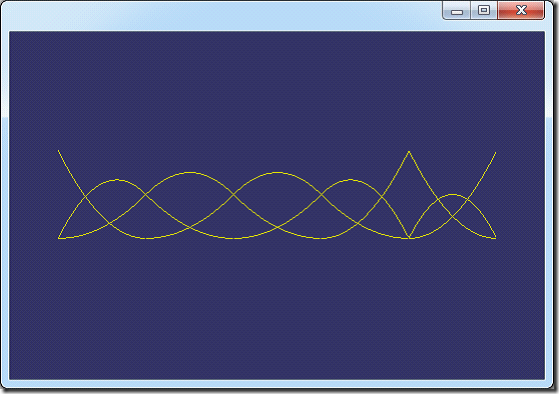
图2. 二次B样条基函数
本来还想将不同的B样条基函数以不同的颜色显示,试了几次,都没有成功。若以不同的颜色显示,会更直观。若你有设置颜色的方法,欢迎告诉我,eryar@163.com。
三、结论 Conclusion
程序计算结果与书中吻合,效果还不错。
理解了B样条的Cox-deBoor递推定义之后,可以将程序中的递归代码转换为非递归实现,这样就可以深入理解B样条基函数了。