最通俗的理解:表示使目标函数取最小值时的变量值
From
Wikipedia
In mathematics, arg max (or argmax) stands for the argument of the maximum, that is to say, the set of points of the given argument for which the value of the given expression attains its maximum value:[note 1]
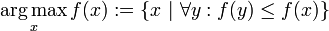
In other words,

is the set of values of x for which f(x) has the largest value M. For example, if f(x) is 1−|x|, then it attains its maximum value of 1 at x = 0 and only there, so 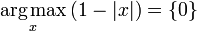 .
.
Equivalently, if M is the maximum of f, then the arg max is the level set of the maximum:

If the maximum is reached at a single value, then one refers to the point as the arg max, meaning we define the arg max as a point, not a set of points. So, for example,
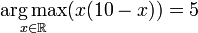
(rather than the singleton set {5}), since the maximum value of x(10 − x) is 25, which happens when x = 5.[note 2]
However, in case the maximum is reached at many values, arg max is a set of points.
Then, we have for example
![\underset{x \in [0,4\pi]}{\operatorname{arg\,max}} \, \cos(x) = \{0,2\pi,4\pi\}](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/0/c/9/0c99d783a9fe097e42c3c38b2a1c0dd5.png)
since the maximum value of cos(x) is 1, which happens on this interval when x = 0, 2π or 4π. On the whole real line, the arg max is 
arg min (or argmin) is defined analogously.
Note also that functions do not in general attain a maximum value, and hence will in general not have an arg max: 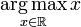 is undefined, as x is unbounded on the real line. However, by the extreme value theorem (or the classical compactness argument), a continuous function on a compact interval has a maximum, and thus an arg max.
is undefined, as x is unbounded on the real line. However, by the extreme value theorem (or the classical compactness argument), a continuous function on a compact interval has a maximum, and thus an arg max.