对图像进行编码有好几种方法。在这里我们考虑2种方法。假设图像只是有黑白两种象素组成,至少有一个黑色象素,而且所有的黑象素都在边界上相连。黑象素不少于1,不多于10。以下为一个例子:
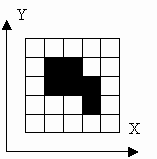
2种编码方法都是只对黑色象素而言。
第一种编码方法:在首行指定黑色象素的个数,以下为每个黑色象素的坐标。象素是以x坐标递增排列的,当x坐标相同时,以y坐标递增顺序给出。上图的编码方法如下:
6
2 3
2 4
3 3
3 4
4 2
4 3
第二种编码方法:首行指定左下角的黑色象素的坐标。以下每行为与它相邻的象素的描述。先是左下角的象素,然后是与它相邻的第一个象素A(如果存在的话),再是与它相邻的第二个象素B(如果存在的话)。当所有相邻的象素都描述完了,接下来就是与A相邻的象素的描述,再是与B相邻的象素的描述,如此类推。
只用一个字母表示相邻,R:在右,T:在上, L:在左,B:在下。一行为一个象素的相邻描述。同一象素不出现2次,如果之前已经描述过,就不用重复描述了。是从右开始,按逆时针方向描述的。每一行的描述以","结束,最后一行的","则改为"."表示文件结束。上图的编码如下:
2 3
RT,
RT,
,
B,
,
.
每一行之前没有空格,结尾也没有空格,在x,y坐标间只有一个空格
input:
给定一种编码方法
output:
输出另一种编码方法
input:
6
2 3
2 4
3 3
3 4
4 2
4 3
output:
2 3
RT,
RT,
,
B,
,
.
【参考程序】:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
const int dx[4]={1,0,-1,0};
const int dy[4]={0,1,0,-1};
const string dir[4]={"R","T","L","B"};
struct node
{
int x,y;
} list[101];
int MAP[11][11];
int n,head,tail;
bool check1(int xx,int yy)
{
if (xx>=1 && xx<=n && yy>=1 && yy<=n && MAP[xx][yy]==1)
return true;
return false;
}
void BFS1(int xx,int yy)
{
head=tail=1;list[1].x=xx;list[1].y=yy;
MAP[xx][yy]=0;
while (head<=tail)
{
for (int i=0;i<=3;i++)
{
int tx,ty;
tx=list[head].x+dx[i];
ty=list[head].y+dy[i];
if (check1(tx,ty))
{
tail++;
list[tail].x=tx;list[tail].y=ty;
cout<<dir[i];
MAP[tx][ty]=-1;
}
}
if (head==tail) cout<<"."<<endl;
else cout<<","<<endl;
head++;
}
}
void add(int xx,int yy)
{
if (!MAP[xx][yy])
{
tail++;
list[tail].x=xx;list[tail].y=yy;
}
}
int cmp(const void *s,const void *t)
{
node i=*(node *)s,j=*(node *)t;
if (i.x!=j.x) return i.x-j.x;
else return i.y-j.y;
}
int main()
{
string s;
getline(cin,s);
memset(MAP,0,sizeof(MAP));
if (s.size()<=2)
{
if (s.size()==1) n=s[0]-'0';
else n=(s[0]-'0')*10+s[1]-'0';
int x,y,a,b;
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>x>>y;
if (i==1)
{
a=x;b=y;
}
MAP[x][y]=1;
}
cout<<a<<" "<<b<<endl;
BFS1(a,b);
}
else
{
int p=s.find(" ");
int n=0,m=0;
for (int i=0;i<p;i++) n=n*10+s[i]-'0';
for (int i=p+1;i<s.size();i++) m=m*10+s[i]-'0';
list[1].x=n;list[1].y=m;head=tail=1;
int tx,ty;
while (head<=tail)
{
getline(cin,s);
for (int i=0;i<s.size();i++)
if (s[i]=='R')
{
tx=list[head].x+1;ty=list[head].y;
add(tx,ty);
}
else if (s[i]=='T')
{
tx=list[head].x;ty=list[head].y+1;
add(tx,ty);
}
else if (s[i]=='L')
{
tx=list[head].x-1;ty=list[head].y;
add(tx,ty);
}
else if (s[i]=='B')
{
tx=list[head].x;ty=list[head].y-1;
add(tx,ty);
}
head++;
}
cout<<tail<<endl;
qsort(list+1,tail,sizeof(node),cmp);
for (int i=1;i<=tail;i++)
cout<<list[i].x<<" "<<list[i].y<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

|