本文剖析hash.h/c,从源代码来剖析eSNACC哈希结构的设计和实现。
为什么要在这里剖析hash呢?一个顺理成章的理由是:我们准备剖析eSNACC对ANY(s)类型的编码和解码,可是ANY的实现依赖于hash,所以我们就需要先把这条路打通了。O(∩_∩)O哈哈~是不是很有说服力呀?
好,闲话少述,言规正传。我们知道hash对一个系统而言,一般都是一个很有价值的底层基础设施。从作用上来说,他实现的优劣极大的影响着整个系统的性能。从技术上来说,也是很能体现含金量的一个模块。所以,对eSNACC实现的这个宝藏,我们下定决心要刨根问底、直捣黄龙!
友情说明:本文不讨论eSNACC用的hash函数,因为我们用了另外独立的一篇文章来研究:剖析eSNACC的hash函数。本文研究的是eSNACC哈希结构的设计和实现。
先看头文件:
 #ifndef _asn_hash_h_
#ifndef _asn_hash_h_
 #define _asn_hash_h_
#define _asn_hash_h_

 #ifdef __cplusplus
#ifdef __cplusplus

 extern "C"
extern "C"  {
{
 #endif
#endif


 #define TABLESIZE 256
#define TABLESIZE 256
 #define INDEXMASK 0xFF
#define INDEXMASK 0xFF
 #define INDEXSHIFT 8
#define INDEXSHIFT 8

 typedef void *Table[TABLESIZE];
typedef void *Table[TABLESIZE];

 typedef unsigned int Hash;
typedef unsigned int Hash;

 typedef struct HashSlot
typedef struct HashSlot


 {
{
 int leaf;
int leaf;
 Hash hash;
Hash hash;
 void *value;
void *value;
 Table *table;
Table *table;
 } HashSlot;
} HashSlot;

 Hash MakeHash PROTO ((char *str, unsigned long len));
Hash MakeHash PROTO ((char *str, unsigned long len));

 Table *InitHash();
Table *InitHash();

 int Insert PROTO ((Table *table, void *element, Hash hash));
int Insert PROTO ((Table *table, void *element, Hash hash));

 int CheckFor PROTO ((Table *table, Hash hash));
int CheckFor PROTO ((Table *table, Hash hash));

 int CheckForAndReturnValue PROTO ((Table *table, Hash hash, void **value));
int CheckForAndReturnValue PROTO ((Table *table, Hash hash, void **value));

 #ifdef __cplusplus
#ifdef __cplusplus
 }
}
 #endif
#endif

 #endif /* conditional include */
#endif /* conditional include */在这里,就利用这个头文件,我想先和大家讲清楚eSNACC的hash表的设计结构。
首先,eSNACC的每一个hash值用unsigned int来定义:typedef unsigned int Hash。
然后,定义的hash表结构——Table:typedef void *Table[TABLESIZE],是一个256维的指针数组。
那这个数组每个元素的内容是什么呢?是指向HashSlot结构的指针,也就是这个hash表的每一维是一个HashSlot。但是如果这样,只能存放256个值呀,怎样实现hash的呢?这个我们就要理解HashSlot的各个变量的意义了:
int leaf : 当前HashSlot是不是树的叶子。
Hash hash :当前HashSlot元素的hash值。
void *value :对应当前hash值元素内容,也就是实际值。
Table *table :如果当前HashSlot不是叶子,也就是说在当前hash有多个共用的元素,那么本字段就不为空,而是指向再次hash的表。
我做了一张简单的示意图来描述:
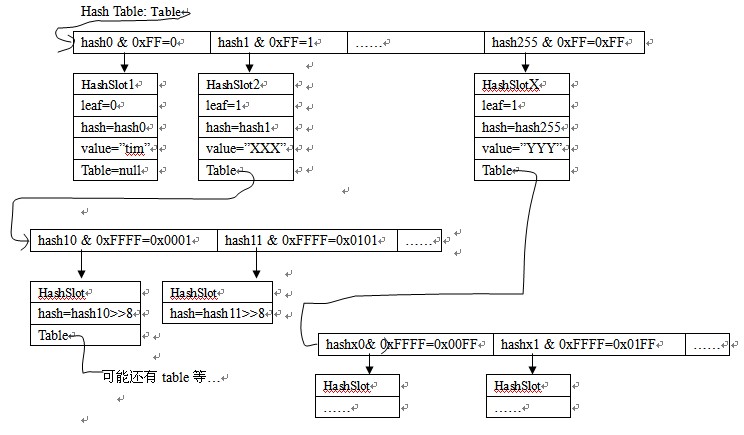
虽然不美观,但还是希望你能从中看明白这个hash表的结构哦。
/******************************休息一下************************************
好了,有了对整个hash表设计的理解,我们就来研究具体的hash表操作函数

 /**//* Creates and clears a new hash slot */
/**//* Creates and clears a new hash slot */
 static HashSlot * NewHashSlot()
static HashSlot * NewHashSlot()


 {
{
 HashSlot *foo;
HashSlot *foo;

 foo = new HashSlot;
foo = new HashSlot;
 if (foo == NULL)
if (foo == NULL)
 return NULL;
return NULL;
 memset (foo, 0, sizeof (HashSlot));
memset (foo, 0, sizeof (HashSlot));
 return foo;
return foo;
 }
}


 /**//* Create a new cleared hash table */
/**//* Create a new cleared hash table */
 static Table *NewTable()
static Table *NewTable()


 {
{
 Table *new_table;
Table *new_table;

 // new_table = new Table;
// new_table = new Table;
 // whose bug is it that gcc won't compile the above line?
// whose bug is it that gcc won't compile the above line?
 new_table = (Table *) new Table;
new_table = (Table *) new Table;
 if (new_table == NULL)
if (new_table == NULL)
 return NULL;
return NULL;
 memset (new_table, 0, sizeof (Table));
memset (new_table, 0, sizeof (Table));
 return new_table;
return new_table;
 }
}


 /**//* This routine is used to initialize the hash tables. When it is called
/**//* This routine is used to initialize the hash tables. When it is called
 * it returns a value which is used to identify which hash table
* it returns a value which is used to identify which hash table
 * a particular request is to operate on.
* a particular request is to operate on.
 */
*/
 Table * InitHash()
Table * InitHash()


 {
{
 Table *table;
Table *table;
 table = NewTable();
table = NewTable();
 if (table == NULL)
if (table == NULL)
 return 0;
return 0;
 else
else
 return table;
return table;
 }
}上面三个很简单,前两个调用new创建HashSlot和Table,第三个就是用来初始最上层hash表的函数。
下面我们来看看将一个hash值为hash_value的元素element插入到哈希表table的具体实现:

 /**//* This routine takes a hash table identifier, an element (value) and the
/**//* This routine takes a hash table identifier, an element (value) and the
 * coresponding hash value for that element and enters it into the table
* coresponding hash value for that element and enters it into the table
 * assuming it isn't already there.
* assuming it isn't already there.
 */
*/
 int Insert (Table *table, void *element, Hash hash_value)
int Insert (Table *table, void *element, Hash hash_value)


 {
{
 HashSlot *entry;
HashSlot *entry;

 entry = (HashSlot *) (*table)[hash_value & INDEXMASK];
entry = (HashSlot *) (*table)[hash_value & INDEXMASK];


 if (entry == NULL)
if (entry == NULL)  {
{

 /**//* Need to add this element here */
/**//* Need to add this element here */
 entry = NewHashSlot();
entry = NewHashSlot();
 if (entry == NULL)
if (entry == NULL)
 return false;
return false;
 entry->leaf = true;
entry->leaf = true;
 entry->value = element;
entry->value = element;
 entry->hash = hash_value;
entry->hash = hash_value;
 (*table)[hash_value & INDEXMASK] = entry;
(*table)[hash_value & INDEXMASK] = entry;
 return true;
return true;
 }
}

 if (hash_value == entry->hash)
if (hash_value == entry->hash)
 return false;
return false;

 if (entry->leaf)
if (entry->leaf)
 return SplitAndInsert (entry, element, hash_value);
return SplitAndInsert (entry, element, hash_value);

 return Insert (entry->table, element, hash_value >> INDEXSHIFT);
return Insert (entry->table, element, hash_value >> INDEXSHIFT);
 }
}函数利用hash_value的最后一个字节来判断该元素应该放在table中的维数,并且取出该维对应的HashSlot entry。
如果entry为空,那么也就是对应该hash_value还没有元素,可以直接创建HashSlot,设定entry的value为element,hash为hash_value,因为当前只有这一个值,所以本HashSlot就是叶子,其table成员也为空。然后将该新的entry连到table的对应维上,完成。
如果entry不为空,依次判断以下三种情况:
1、如果当前entry的hash等于hash_value,那就是hash值冲突,直接返回false。
2、如果当前entry是叶子,那么就得拆分当前HashSlot,使得他用table来存放多个值。
3、如果entry不是叶子了,那么就将本元素插到entry->table里面。
我们看一下SplitAndInsert:

 /**//* When a hash collision occurs at a leaf slot this routine is called to
/**//* When a hash collision occurs at a leaf slot this routine is called to
 * split the entry and add a new level to the tree at this point.
* split the entry and add a new level to the tree at this point.
 */
*/
 static int SplitAndInsert (HashSlot *entry, void *element, Hash hash_value)
static int SplitAndInsert (HashSlot *entry, void *element, Hash hash_value)


 {
{

 if (((entry->table = NewTable()) == NULL) ||
if (((entry->table = NewTable()) == NULL) ||
 !Insert (entry->table, entry->value, entry->hash >> INDEXSHIFT) ||
!Insert (entry->table, entry->value, entry->hash >> INDEXSHIFT) ||
 !Insert (entry->table, element, hash_value >> INDEXSHIFT))
!Insert (entry->table, element, hash_value >> INDEXSHIFT))
 return false;
return false;

 entry->leaf = false;
entry->leaf = false;
 return true;
return true;
 }
}恩,很清楚,首先为entry的table分配一个Table,接着再将entry中原来存的值(entry->vlaue,entry->hash)插到表里,然后还将新加入的值(element,hash_value)插入表里。最后将entry的叶子属性改为非叶子。
注意:在级联的hash表里存的不是原来的hash值,而是依次将hash>>8.也就是出了最高层的哈希表,其他的都依次去掉最末尾的一个字节!!!
我们模拟插入两个元素,假设其值和hash分别为A("tim",0xAA02),B("eSNACC",0xBB02).只是为了说明,我们假设原始table为空:
1,插入A:hash_value=0xAA02,所以应当插入到table的第三维,插入以后应当为:
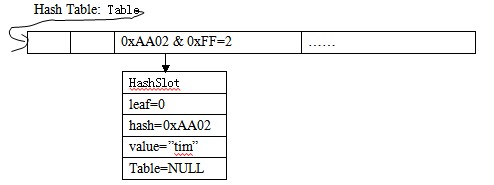
2.插入B:hash_value=0xBB02,hash_value & 0xFF=2,所以又找到第三位,然后此时有HashSlot叶子,所以需要拆分,在插入后应当为:
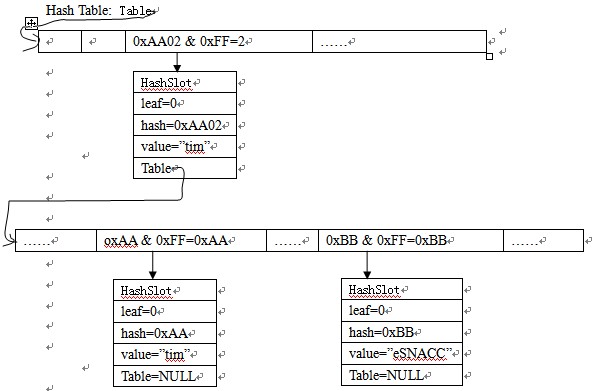
利用这两个图,应该说得很清楚了吧,还是图最清楚了!O(∩_∩)O哈哈~
好了,让我们来看最后两个函数:

 /**//* This routine looks to see if a particular hash value is already stored in
/**//* This routine looks to see if a particular hash value is already stored in
 * the table. It returns true if it is and false otherwise.
* the table. It returns true if it is and false otherwise.
 */
*/
 int CheckFor (Table *table, Hash hash)
int CheckFor (Table *table, Hash hash)


 {
{
 HashSlot *entry;
HashSlot *entry;

 entry = (HashSlot *) table[hash & INDEXMASK];
entry = (HashSlot *) table[hash & INDEXMASK];

 if (entry == NULL)
if (entry == NULL)
 return false;
return false;
 if (entry->leaf)
if (entry->leaf)
 return entry->hash == hash;
return entry->hash == hash;
 return CheckFor (entry->table, hash >> INDEXSHIFT);
return CheckFor (entry->table, hash >> INDEXSHIFT);
 }
}


 /**//* In addition to checking for a hash value in the tree this function also
/**//* In addition to checking for a hash value in the tree this function also
 * returns the coresponding element value into the space pointed to by
* returns the coresponding element value into the space pointed to by
 * the value parameter. If the hash value isn't found false is returned
* the value parameter. If the hash value isn't found false is returned
 * the the space pointed to by value is not changed.
* the the space pointed to by value is not changed.
 */
*/
 int CheckForAndReturnValue (Table *table, Hash hash, void **value)
int CheckForAndReturnValue (Table *table, Hash hash, void **value)


 {
{
 HashSlot *entry;
HashSlot *entry;
 if (table)
if (table)


 {
{
 entry = (HashSlot *) (*table)[hash & INDEXMASK];
entry = (HashSlot *) (*table)[hash & INDEXMASK];

 if (entry == NULL)
if (entry == NULL)
 return false;
return false;

 if (entry->leaf)
if (entry->leaf)


 {
{
 if (entry->hash == hash)
if (entry->hash == hash)


 {
{
 *value = entry->value;
*value = entry->value;
 return true;
return true;
 }
}
 else
else
 return false;
return false;
 }
}
 return CheckForAndReturnValue (entry->table, hash >> INDEXSHIFT, value);
return CheckForAndReturnValue (entry->table, hash >> INDEXSHIFT, value);
 }
}
 else
else
 return false;
return false;
 }
}这两个函数功能很清晰,就是在给定的哈希表table查找对应哈希值为hash的元素。只是CheckFor只是检查table存在此hash否。而CheckForAndReturnValue则在存在时,将元素值存在value中返回。
好了,到此,eSNACC哈希结构的设计就已经全部分析完成了!祝大家学习愉快~