| |
常用链接
留言簿(4)
随笔分类
随笔档案
搜索
最新评论

阅读排行榜
评论排行榜
Powered by: 博客园
模板提供:沪江博客
|
|
|
|
|
发新文章 |
|
 | |

给定a,b,设G=gcd(a,b),于是有a=A*G,b=B*G(1<=A,B,gcd(A,B)=1) 对于a的多次加可以看成K*a(1<=k),转化成(K*a)%b的所有结果能否表示成0..b-1中的所有数, 假(K*a)%b=M,M=K*a-W*b(W为使M>0的最大整数),M=K*A*G-W*B*G M%G==0, 既结果是G的倍数,如果想取得0..b-1中的所有数, 那么必须G=1才可能.. 这算法牛X。。。
 #include"stdio.h" #include"stdio.h"
 int main() int main()
   { {
 long m,n,k,i; long m,n,k,i;
 while(scanf("%ld%ld",&m,&n)!=-1) while(scanf("%ld%ld",&m,&n)!=-1)
   { printf("%10ld%10ld ",m,n); { printf("%10ld%10ld ",m,n);
 k=1; k=1;
 for(i=2;i<=(m>n?n:m);i++) for(i=2;i<=(m>n?n:m);i++)
   { {
 if(m%i==0&&n%i==0) if(m%i==0&&n%i==0)
 k=i; k=i;
 } }
 if(k==1) if(k==1)
 printf("Good Choice\n\n"); printf("Good Choice\n\n");
 else else
 printf("Bad Choice\n\n"); printf("Bad Choice\n\n");

 } }
 } }
妈的,没见过那么恶心的题目。。。 首先题目就错了,1不是质数啊!!! 输出之间居然还有一空行。。。 检查了半天都没查出来,杀人了!!! 懒得改了,用了同学的
 #include <iostream> #include <iostream>
 #include <vector> #include <vector>
 #include <string> #include <string>
 #include <math.h> #include <math.h>
 #include <iomanip> #include <iomanip>
 #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdlib.h>
 using namespace std; using namespace std;

 #include"stdio.h" #include"stdio.h"
 #include"math.h" #include"math.h"
 int p[2001]; int p[2001];

 int main() int main()
   { {
 int n,c,n1; int n,c,n1;
 int i,j; int i,j;
 int tol; int tol;
 int flag; int flag;
 while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&c)!=-1) while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&c)!=-1)
   { {


 p[1]=1; p[1]=1;
 tol=1; tol=1;
 for(i=2;i<=3000;i++) for(i=2;i<=3000;i++)
   { {
 flag=1; flag=1;
 for(j=2;j<=(int)sqrt((double)i);j++) for(j=2;j<=(int)sqrt((double)i);j++)
   { {
  if(i%j==0) if(i%j==0) {flag=0;break;} {flag=0;break;}
 } }
 if(flag==0)continue; if(flag==0)continue;
 else if(i>n)break; else if(i>n)break;
 else else
   { {
 tol++; tol++;
 p[tol]=i; p[tol]=i;

 } }

 } }


 //此时质数的个数是tol,第一个质数是1 //此时质数的个数是tol,第一个质数是1
 printf("%d %d:",n,c); printf("%d %d:",n,c);
 if(tol%2==0&&tol>=c*2) if(tol%2==0&&tol>=c*2)
   { {
 for(i=1;i<=c*2;i++) for(i=1;i<=c*2;i++)
   { {
 j=(tol-c*2)/2; j=(tol-c*2)/2;
 printf(" %d",p[j+i]); printf(" %d",p[j+i]);

 } }
 printf("\n\n"); printf("\n\n");
 } }

 if(tol%2==0&&tol<c*2) if(tol%2==0&&tol<c*2)
   { {
 for(j=1;j<=tol;j++) for(j=1;j<=tol;j++)
 printf(" %d",p[j]); printf(" %d",p[j]);
 printf("\n\n"); printf("\n\n");
 } }

 if(tol%2==1&&tol>=c*2-1) if(tol%2==1&&tol>=c*2-1)
   { {
 for(i=1;i<=c*2-1;i++) for(i=1;i<=c*2-1;i++)
   { {
 j=(tol-c*2+1)/2; j=(tol-c*2+1)/2;
 printf(" %d",p[i+j]); printf(" %d",p[i+j]);
 } }
 printf("\n\n"); printf("\n\n");
 } }

 if(tol%2==1&&tol<c*2-1) if(tol%2==1&&tol<c*2-1)
   { {
 for(j=1;j<=tol;j++) for(j=1;j<=tol;j++)
   { {
 printf(" %d",p[j]); printf(" %d",p[j]);
 } }
 printf("\n\n"); printf("\n\n");
 } }



 } }
 } }
传说中的动态规划。。。 注意题目的优先计算顺序。先是考虑是否会小于0,然后才考虑是否会大于20,要不然就会WA。 哇塞,真的这样,这题太假了。。。
 #include <iostream> #include <iostream>
 #include <vector> #include <vector>
 #include <string> #include <string>
 #include <math.h> #include <math.h>
 #include <iomanip> #include <iomanip>
 #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdlib.h>
 using namespace std; using namespace std;

 int w[21][21][21]; int w[21][21][21];

 void init() void init()
   { {
 for (int i=0;i<21;i++) for (int i=0;i<21;i++)
   { {
 for (int j=0;j<21;j++) for (int j=0;j<21;j++)
   { {
 for (int k=0;k<21;k++) for (int k=0;k<21;k++)
   { {
 if(i==0||j==0||k==0) if(i==0||j==0||k==0)
 w[i][j][k]=1; w[i][j][k]=1;
 else if(i<j&&j<k) else if(i<j&&j<k)
 w[i][j][k]=w[i][j][k-1]+w[i][j-1][k-1]-w[i][j-1][k]; w[i][j][k]=w[i][j][k-1]+w[i][j-1][k-1]-w[i][j-1][k];
 else else
 w[i][j][k]=w[i-1][j][k]+w[i-1][j-1][k]+w[i-1][j][k-1]-w[i-1][j-1][k-1]; w[i][j][k]=w[i-1][j][k]+w[i-1][j-1][k]+w[i-1][j][k-1]-w[i-1][j-1][k-1];
 } }
 } }
 } }
 } }
 int main() int main()
   { {
 init(); init();
 int a,b,c; int a,b,c;
 while (scanf("%d %d %d",&a,&b,&c)!=EOF) while (scanf("%d %d %d",&a,&b,&c)!=EOF)
   { {
 if (a==-1&&b==-1&&c==-1) if (a==-1&&b==-1&&c==-1)
   {break; {break;
 } }
 if (a<=0||b<=0||c<=0) if (a<=0||b<=0||c<=0)
   { {
 printf("w(%d, %d, %d) = %d\n",a,b,c,w[0][0][0]); printf("w(%d, %d, %d) = %d\n",a,b,c,w[0][0][0]);
 } }
 else if (a>20||b>20||c>20) else if (a>20||b>20||c>20)
   { {
 printf("w(%d, %d, %d) = %d\n",a,b,c,w[20][20][20]); printf("w(%d, %d, %d) = %d\n",a,b,c,w[20][20][20]);
 } }
 else else
   { {
 printf("w(%d, %d, %d) = %d\n",a,b,c,w[a][b][c]); printf("w(%d, %d, %d) = %d\n",a,b,c,w[a][b][c]);
 } }
 } }
 } }
Trie树就是字典树,其核心思想就是空间换时间。
举个简单的例子。
给你100000个长度不超过10的单词。对于每一个单词,我们要判断他出没出现过,如果出现了,第一次出现第几个位置。
这题当然可以用hash来,但是我要介绍的是trie树。在某些方面它的用途更大。比如说对于某一个单词,我要询问它的前缀是否出现过。这样hash就不好搞了,而用trie还是很简单。
现在回到例子中,如果我们用最傻的方法,对于每一个单词,我们都要去查找它前面的单词中是否有它。那么这个算法的复杂度就是O(n^2)。显然对于100000的范围难以接受。现在我们换个思路想。假设我要查询的单词是abcd,那么在他前面的单词中,以b,c,d,f之类开头的我显然不必考虑。而只要找以a开头的中是否存在abcd就可以了。同样的,在以a开头中的单词中,我们只要考虑以b作为第二个字母的……这样一个树的模型就渐渐清晰了……
假设有b,abc,abd,bcd,abcd,efg,hii这6个单词,我们构建的树就是这样的。
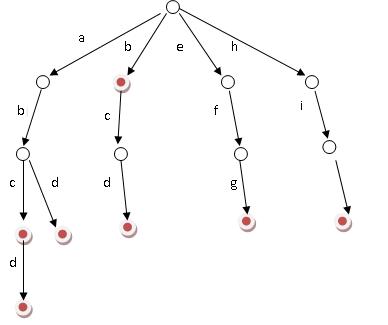
对于每一个节点,从根遍历到他的过程就是一个单词,如果这个节点被标记为红色,就表示这个单词存在,否则不存在。
那么,对于一个单词,我只要顺着他从跟走到对应的节点,再看这个节点是否被标记为红色就可以知道它是否出现过了。把这个节点标记为红色,就相当于插入了这个单词。
这样一来我们询问和插入可以一起完成,所用时间仅仅为单词长度,在这一个样例,便是10。
我们可以看到,trie树每一层的节点数是26^i级别的。所以为了节省空间。我们用动态链表,或者用数组来模拟动态。空间的花费,不会超过单词数×单词长度。
给出一个用类封装的字典树代码,厄。。。做ACM的模板用另一个。。应该放在了“ACM模板”文件夹下了。。。
 #include <cstdio> #include <cstdio>
 #include <iostream> #include <iostream>
 #include <cstring> #include <cstring>
 using namespace std; using namespace std;


 const int num_chars = 26; const int num_chars = 26;


  class Trie class Trie  { {
 public: public:
  Trie():root(NULL) Trie():root(NULL) {}; {};
 Trie(Trie& tr); Trie(Trie& tr);

 int search(const char* word, char* entry ) const; int search(const char* word, char* entry ) const;
 int insert(const char* word, const char* entry); int insert(const char* word, const char* entry);
 int remove(const char* word, char* entry); int remove(const char* word, char* entry);
 private: private:
 struct Trie_node struct Trie_node
   { {
 char* data; char* data;
 Trie_node* branch[num_chars]; Trie_node* branch[num_chars];
 Trie_node(); Trie_node();
 }* root; }* root;
 }; };
 Trie::Trie_node::Trie_node() Trie::Trie_node::Trie_node()
   { {
 data = NULL; data = NULL;
 for (int i=0; i<num_chars; ++i) for (int i=0; i<num_chars; ++i)
 branch[i] = NULL; branch[i] = NULL;
 } }

 int Trie::search(const char* word, char* entry ) const int Trie::search(const char* word, char* entry ) const
   { {
 int position = 0; int position = 0;
 char char_code; char char_code;
 Trie_node *location = root; Trie_node *location = root;
 while( location!=NULL && *word!=0 ) while( location!=NULL && *word!=0 )
   { {
 if (*word>='A' && *word<='Z') if (*word>='A' && *word<='Z')
 char_code = *word-'A'; char_code = *word-'A';
 else if (*word>='a' && *word<='z') else if (*word>='a' && *word<='z')
 char_code = *word-'a'; char_code = *word-'a';
 else return 0; else return 0;


 location = location->branch[char_code]; location = location->branch[char_code];
 position++; position++;
 word++; word++;
 } }
 if ( location != NULL && location->data != NULL ) if ( location != NULL && location->data != NULL )
   { {
 strcpy(entry,location->data); strcpy(entry,location->data);
 return 1; return 1;
 } }
 else return 0; else return 0;
 } }
 int Trie::insert(const char* word, const char* entry) int Trie::insert(const char* word, const char* entry)
   { {
 int result = 1, position = 0; int result = 1, position = 0;
 if ( root == NULL ) root = new Trie_node; if ( root == NULL ) root = new Trie_node;
 char char_code; char char_code;
 Trie_node *location = root; Trie_node *location = root;
 while( location!=NULL && *word!=0 ) while( location!=NULL && *word!=0 )
   { {
 if (*word>='A' && *word<='Z') if (*word>='A' && *word<='Z')
 char_code = *word-'A'; char_code = *word-'A';
 else if (*word>='a' && *word<='z') else if (*word>='a' && *word<='z')
 char_code = *word-'a'; char_code = *word-'a';
 else return 0; else return 0;


 if( location->branch[char_code] == NULL ) if( location->branch[char_code] == NULL )
 location->branch[char_code] = new Trie_node; location->branch[char_code] = new Trie_node;


 location = location->branch[char_code]; location = location->branch[char_code];
 position++; position++;
 word++; word++;
 } }
 if (location->data != NULL) if (location->data != NULL)
 result = 0; result = 0;
  else else  { {
 location->data = new char[strlen(entry)+1]; location->data = new char[strlen(entry)+1];
 strcpy(location->data, entry); strcpy(location->data, entry);
 } }
 return result; return result;
 } }
 int main() int main()
   { {
 Trie t; Trie t;
 char entry[100]; char entry[100];
 t.insert("aa", "DET"); t.insert("aa", "DET");
 t.insert("abacus","NOUN"); t.insert("abacus","NOUN");
 t.insert("abalone","NOUN"); t.insert("abalone","NOUN");
 t.insert("abandon","VERB"); t.insert("abandon","VERB");
 t.insert("abandoned","ADJ"); t.insert("abandoned","ADJ");
 t.insert("abashed","ADJ"); t.insert("abashed","ADJ");
 t.insert("abate","VERB"); t.insert("abate","VERB");
 t.insert("this", "PRON"); t.insert("this", "PRON");
 if (t.search("this", entry)) if (t.search("this", entry))
 cout<<"'this' was found. pos: "<<entry<<endl; cout<<"'this' was found. pos: "<<entry<<endl;
 if (t.search("abate", entry)) if (t.search("abate", entry))
 cout<<"'abate' is found. pos: "<<entry<<endl; cout<<"'abate' is found. pos: "<<entry<<endl;
 if (t.search("baby", entry)) if (t.search("baby", entry))
 cout<<"'baby' is found. pos: "<<entry<<endl; cout<<"'baby' is found. pos: "<<entry<<endl;
 else else
 cout<<"'baby' does not exist at all!"<<endl; cout<<"'baby' does not exist at all!"<<endl;

 if (t.search("aa", entry)) if (t.search("aa", entry))
 cout<<"'aa was found. pos: "<<entry<<endl; cout<<"'aa was found. pos: "<<entry<<endl;
 } }

 PS:实现方法 http://met.fzu.edu.cn/eduonline/web/web/resources/articleContent.asp?id=346
摘要: 今天总算是碰到一道复杂题了。。。(我BT了?)弄死我了,主要是排除重复情况,我想不通,最后参考了前人的代码,修改后AC了。。。思路:通过递归,得出可能存在的解法,并记录,查找原记录,若存在相同则取消记录
#include <iostream>#include <vector>#include <string>#include&nb... 阅读全文
<本文中排序都是采用的从小到大排序>
一、对int类型数组排序
程序代码 程序代码
int num[100];
Sample:
int cmp ( const void *a , const void *b )
{
return *(int *)a - *(int *)b;
}
qsort(num,100,sizeof(num[0]),cmp);
二、对char类型数组排序(同int类型)
程序代码 程序代码
char word[100];
Sample:
int cmp( const void *a , const void *b )
{
return *(char *)a - *(char*)b;
}
qsort(word,100,sizeof(word[0]),cmp)
三、对double类型数组排序(特别要注意)
程序代码 程序代码
double in[100];
int cmp( const void *a , const void *b )
{
return *(double *)a > *(double *)b ? 1 : -1;
} qsort(in,100,sizeof(in[0]),cmp);
四、对结构体一级排序
程序代码 程序代码
struct In {
double data;
int other;
}s[100]
//按照data的值从小到大将结构体排序,关于结构体内的排序关键数据data的类型可以很多种,
参考上面的例子写
int cmp( const void *a ,const void *b)
{
return (*(In *)a).data > (*(In *)b).data ? 1 : -1;
}
qsort(s,100,sizeof(s[0]),cmp);
五、对结构体二级排序
程序代码 程序代码
struct In {
int x; int y;
}s[100];
//按照x从小到大排序,当x相等时按照y从大到小排序
int cmp( const void *a , const void *b )
{
struct In *c = (In *)a;
struct In *d = (In *)b;
if(c->x != d->x) return c->x - d->x;
else return d->y - c->y;
}
qsort(s,100,sizeof(s[0]),cmp);
六、对字符串进行排序
程序代码 程序代码
struct In {
int data; char str[100];
}s[100];
//按照结构体中字符串str的字典顺序排序
int cmp ( const void *a , const void *b )
{
return strcmp( (*(In *)a)->str , (*(In *)b)->str );
}
qsort(s,100,sizeof(s[0]),cmp);
七、计算几何中求凸包的cmp
程序代码 程序代码
int cmp(const void *a,const void *b)
//重点cmp函数,把除了1点外的所有点,旋转角度排序
{
struct point *c=(point *)a;
struct point *d=(point *)b;
if( calc(*c,*d,p[1]) < 0) return 1;
else if( !calc(*c,*d,p[1])
&& dis(c->x,c->y,p[1].x,p[1].y) < dis(d->x,d->y,p[1].x,p[1].y))
//如果在一条直线上,则把远的放在前面
return 1; else return -1;
}
PS: 其中的qsort函数包含在<stdlib.h>的头文件里,strcmp包含在<string.h>的头文件里
|
|