发现简单的测试还是比较好用的,于是考虑重写代码,取消库前缀,做一些库结构上的改变.
暂时先不考虑写内存泄露检测库.
等有空,可以再把测试时测试代码自动输出测试文档的部分写下.

 #ifdef TEST_OPEN
#ifdef TEST_OPEN


 #ifndef TEST__
#ifndef TEST__
 #define TEST__
#define TEST__


 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>

 using std::cout;
using std::cout;
 using std::endl;
using std::endl;






 #define FLAG__ cout<<"[test:flag]";
#define FLAG__ cout<<"[test:flag]";

 #define SHOW__(X) cout<<X<<endl;
#define SHOW__(X) cout<<X<<endl;



 #define TEST_THROW(X) throw string(X);
#define TEST_THROW(X) throw string(X);
 #define TEST_BEGIN try{
#define TEST_BEGIN try{
 #define TEST_END }catch(string TEST_CATCH){ cout<<TEST_CATCH<<endl;}
#define TEST_END }catch(string TEST_CATCH){ cout<<TEST_CATCH<<endl;}


 #endif
#endif
 #endif
#endif

 #ifndef TEST_OPEN
#ifndef TEST_OPEN

 #define TEST_BEGIN
#define TEST_BEGIN
 #define TEST_END
#define TEST_END
 #define TEST_THROW(X)
#define TEST_THROW(X)
 #define SHOW__(X)
#define SHOW__(X)
 #define FLAG__
#define FLAG__


 #endif
#endif



让测试能够原封不动的保留其代码而不需要在不需要的时候注释掉他们 只需要通过一条#define TEST_OPEN 启动或者关闭其功能.
TEST_BEGIN / TEST_END 用于获取库调用时出现的库使用者越界或者其他极端条件下造成的异常.
对于自己宏的命名规则只两种:
XXX_XXXX :
XXXX__

 #define TEST_OPEN
#define TEST_OPEN



 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
 #include <string>
#include <string>

 using namespace std;
using namespace std;

 #include "base.h"
#include "base.h"
 #include "ptr.h"
#include "ptr.h"
 #include "runtime.h"
#include "runtime.h"
 #include "tree.h"
#include "tree.h"
 #include "array.h"
#include "array.h"
 #include "vector.h"
#include "vector.h"



 void test_runtime()
void test_runtime()


 {
{
 using os::chaos;
using os::chaos;
 using os::runtime;
using os::runtime;
 chaos c;
chaos c;
 runtime t_;
runtime t_;
 t_.begin();
t_.begin();
 for(int i=0;i!=1110;i++)
for(int i=0;i!=1110;i++)
 cout<<c.getRandom(5,10)<<endl;
cout<<c.getRandom(5,10)<<endl;
 t_.end();
t_.end();
 cout<<"get time:"<<t_.getDTime()<<"ms"<<endl;
cout<<"get time:"<<t_.getDTime()<<"ms"<<endl;
 }
}
 void test_ptr()
void test_ptr()


 {
{

 using code::ptr;
using code::ptr;

 ptr<string> str,str2;
ptr<string> str,str2;
 str ="lost butterfly.";
str ="lost butterfly.";
 str2=str;
str2=str;
 cout<<str()<<endl
cout<<str()<<endl
 <<str2()<<endl;
<<str2()<<endl;
 str2.free();
str2.free();
 cout<<str()<<endl;
cout<<str()<<endl;

 }
}

 void test_tree()
void test_tree()


 {
{
 using adt::tree;
using adt::tree;
 tree<int> t,t2;
tree<int> t,t2;
 t.set(1);
t.set(1);
 t.goLeft(1);
t.goLeft(1);
 t.goRight(2);
t.goRight(2);
 t.setLeft(3);
t.setLeft(3);
 t.setRight(4);
t.setRight(4);

 int list[10]=
int list[10]= {0},list2[20]=
{0},list2[20]= {0};
{0};
 t.travel(list,1);
t.travel(list,1);
 for(int i=0;i!=t.n;i++)
for(int i=0;i!=t.n;i++)
 cout<<list[i]<<endl;
cout<<list[i]<<endl;
 t2=t;
t2=t;
 t2.travel(list2,1);
t2.travel(list2,1);
 cout<<":\n";
cout<<":\n";

 for(int i=0;i!=t2.n;i++)
for(int i=0;i!=t2.n;i++)
 cout<<list2[i]<<endl;
cout<<list2[i]<<endl;
 }
}

 void test_array()
void test_array()


 {
{
 using adt::array;
using adt::array;

 array<int> ar(5,0),ar2(10,1);
array<int> ar(5,0),ar2(10,1);

 ar[0]=1;
ar[0]=1;
 ar[1]=2;
ar[1]=2;
 ar[4]=3;
ar[4]=3;
 for(int i=0;i!=ar.n_;i++)
for(int i=0;i!=ar.n_;i++)
 cout<<ar[i]<<endl;
cout<<ar[i]<<endl;
 ar=ar2;
ar=ar2;
 ar2[3]=2;
ar2[3]=2;
 for(int i=0;i!=ar2.n_;i++)
for(int i=0;i!=ar2.n_;i++)
 cout<<ar2[i]<<endl;
cout<<ar2[i]<<endl;
 }
}
 void test_vector()
void test_vector()


 {
{
 using adt::vector;
using adt::vector;

 vector<int> v,v2;
vector<int> v,v2;
 v2.push(3);
v2.push(3);
 v2.push(4);
v2.push(4);
 v2[1]=5;
v2[1]=5;
 v2.pop();
v2.pop();
 v=v2;
v=v2;
 FLAG__
FLAG__
 cout<<v.pop()<<endl;
cout<<v.pop()<<endl;
 //cout<<v.isNull();
//cout<<v.isNull();

 TEST_BEGIN
TEST_BEGIN
 cout<<v.pop()<<endl;
cout<<v.pop()<<endl;
 TEST_END
TEST_END

 //cout<<v.isNull();
//cout<<v.isNull();
 }
}
 int main()
int main()


 {
{

 test_ptr();
test_ptr();
 test_tree();
test_tree();
 test_runtime();
test_runtime();
 test_array();
test_array();
 test_vector();
test_vector();


 return 1;
return 1;
 }
}


初步对整个库的部分实现顺序和命名规则,1 左边是原则
1 左边是约定
2 右边是实现顺序,从左到右.
临时草稿在这个程度上还是没什么问题的,必要时列出AOV防止实现的冲突
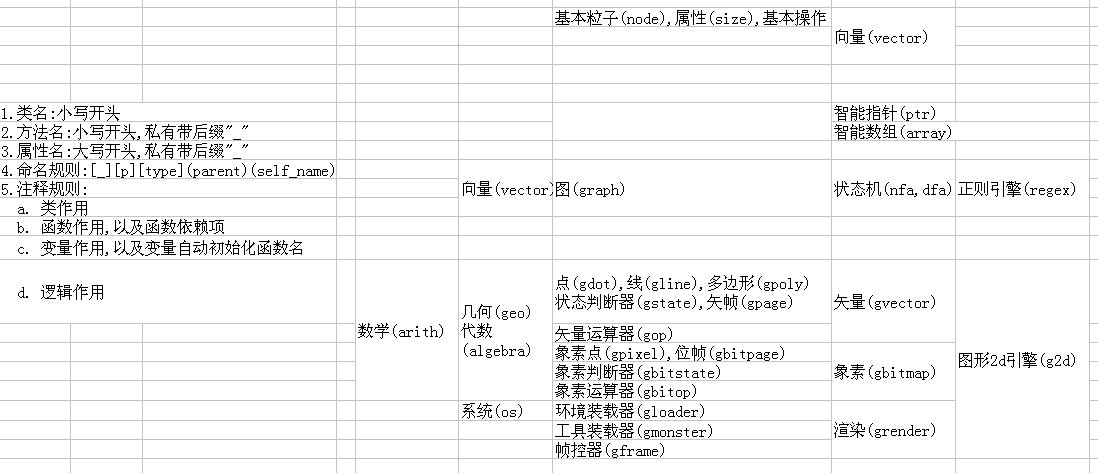
对于表中自己设定的"属性名首字母大写",恐怕我还是喜欢小写.
有的时候为了让库的使用者知道某些封装的属性虽然是public但不应该去擅自修改值的,可以后缀带"_". 成员函数也如此,是内置且开放方法但不推荐直接使用的函数.
另外从现在开始在vector以及以后的所有代码里增加对代码的维护test,
 #ifndef VECTOR__
#ifndef VECTOR__
 #define VECTOR__
#define VECTOR__

 #pragma warning (disable: 4138)
#pragma warning (disable: 4138)

 #include "base.h"//it includes test.h
#include "base.h"//it includes test.h


 namespace adt
namespace adt


 {
{
 #define SMART_INDEX
#define SMART_INDEX
 template<typename VType>
template<typename VType>

 class /**//*Adt: Double Chain Table*/ vector:public base::adt
class /**//*Adt: Double Chain Table*/ vector:public base::adt


 {
{
 public:
public:
 int smartindex(int & _i,const int& _n)
int smartindex(int & _i,const int& _n)


 {
{
 #ifdef SMART_INDEX
#ifdef SMART_INDEX
 if(_n==1)
if(_n==1)


 {
{
 _i=0;
_i=0;
 return 0;
return 0;
 }
}
 if(_i<0)
if(_i<0)


 {
{
 _i=-_i;
_i=-_i;
 _i=_i%_n;
_i=_i%_n;
 _i = _n - _i;
_i = _n - _i;
 }else
}else


 {
{
 _i=_i%_n;
_i=_i%_n;
 }
}
 #endif
#endif
 return 1;
return 1;
 }
}
 typedef struct VNode
typedef struct VNode


 {
{

 VNode*/**//*prior node*/ prev;
VNode*/**//*prior node*/ prev;

 VNode*/**//*following node*/ next;
VNode*/**//*following node*/ next;
 VType elem;
VType elem;
 int extend_prev(VType _prev_elem)
int extend_prev(VType _prev_elem)


 {
{
 prev=new VNode;
prev=new VNode;
 prev->elem=_prev_elem;
prev->elem=_prev_elem;
 prev->next=this;
prev->next=this;

 return 1;
return 1;
 }
}
 int extend_prev()
int extend_prev()


 {
{
 prev=new VNode;
prev=new VNode;
 prev->next=this;
prev->next=this;

 return 1;
return 1;
 }
}
 int extend_next(VType _nextend_elem)
int extend_next(VType _nextend_elem)


 {
{

 next=new VNode;
next=new VNode;

 next->elem=_nextend_elem;
next->elem=_nextend_elem;
 next->prev=this;
next->prev=this;

 return 1;
return 1;
 }
}
 int extend_next()
int extend_next()


 {
{

 next=new VNode;
next=new VNode;
 next->prev=this;
next->prev=this;

 return 1;
return 1;
 }
}
 int inst_node(const VType &_inst_elem)
int inst_node(const VType &_inst_elem)

 /**//* inserts a node between obj and obj's following */
/**//* inserts a node between obj and obj's following */


 {
{
 VNode* _ins_node=new VNode;
VNode* _ins_node=new VNode;
 _ins_node->elem=_inst_elem;
_ins_node->elem=_inst_elem;

 _ins_node->next=this->next;
_ins_node->next=this->next;
 _ins_node->next->prev=_ins_node;
_ins_node->next->prev=_ins_node;
 this->next=_ins_node;
this->next=_ins_node;
 _ins_node->prev=this;
_ins_node->prev=this;
 return 1;
return 1;
 }
}
 int remove()
int remove()

 /**//* deletes the middle node and close its prev and next */
/**//* deletes the middle node and close its prev and next */


 {
{
 if(!this->prev||!this->next)
if(!this->prev||!this->next)


 {
{
 return 0;
return 0;
 }
}
 this->prev->next=this->next;
this->prev->next=this->next;
 this->next->prev=this->prev;
this->next->prev=this->prev;
 delete this;
delete this;
 return 1;
return 1;
 }
}

 };
};




 public :
public :

 VNode* head;
VNode* head;
 VNode* tail;
VNode* tail;
 VNode* p;
VNode* p;
 int n;
int n;
 vector(VType *_init_elem=0,int _len=0)
vector(VType *_init_elem=0,int _len=0)


 {
{


 if(_len<=-1)return;
if(_len<=-1)return;

 p=head=new VNode;
p=head=new VNode;
 p->prev=0;
p->prev=0;


 for(int j=0;j!=_len;j++)
for(int j=0;j!=_len;j++)


 {
{
 p->extend_next(_init_elem[j]);
p->extend_next(_init_elem[j]);
 p=p->next;
p=p->next;
 }
}
 p->extend_next();
p->extend_next();
 n=_len;
n=_len;


 }
}
 int rebirth(VType *_re_init_elem,int _len=0)
int rebirth(VType *_re_init_elem,int _len=0)


 {
{
 vector(_re_init_elem,_len);
vector(_re_init_elem,_len);

 return 1;
return 1;
 }
}

 int index(VType _value)
int index(VType _value)


 {
{

 p=head->next;
p=head->next;
 for(int j=0;j!=n;j++)
for(int j=0;j!=n;j++)


 {
{
 if(p->elem==_value)
if(p->elem==_value)


 {
{
 return j;
return j;
 }
}
 p=p->next;
p=p->next;
 }
}


 return -1;
return -1;
 }
}
 VType & operator [](int _i)
VType & operator [](int _i)


 {
{
 smartindex(_i,n);
smartindex(_i,n);

 p=head->next;
p=head->next;
 for(int j=0;j!=_i;j++)
for(int j=0;j!=_i;j++)


 {
{
 p=p->next;
p=p->next;
 }
}


 return p->elem;
return p->elem;
 }
}

 int insert(int _i,VType _obj_elem)
int insert(int _i,VType _obj_elem)


 {
{
 p=head;
p=head;

 for(int j=0;j!=_i;j++)
for(int j=0;j!=_i;j++)


 {
{
 p=p->next;
p=p->next;
 }
}
 p->inst_node(_obj_elem);
p->inst_node(_obj_elem);

 ++n;
++n;

 return 1;
return 1;
 }
}
 int isNull()
int isNull()


 {
{
 if(n==0)return 1;
if(n==0)return 1;
 else return 0;
else return 0;
 }
}
 int push(VType _obj)
int push(VType _obj)


 {
{
 insert(n,_obj);
insert(n,_obj);
 return 1;
return 1;
 }
}
 VType pop()
VType pop()


 {
{
 #ifdef TEST_OPEN
#ifdef TEST_OPEN
 if(n==0)
if(n==0)
 TEST_THROW("Exception in vector pop-function")
TEST_THROW("Exception in vector pop-function")
 #endif
#endif
 return remove(-1);
return remove(-1);
 }
}
 VType remove(int _i)
VType remove(int _i)


 {
{
 smartindex(_i,n);
smartindex(_i,n);
 p=head->next;
p=head->next;

 for(int j=0;j!=_i;j++)
for(int j=0;j!=_i;j++)


 {
{
 p=p->next;
p=p->next;
 }
}

 VType buf=p->elem;
VType buf=p->elem;

 p->remove();
p->remove();
 --n;
--n;

 return buf;
return buf;

 }
}
 void operator = (vector& _copy)
void operator = (vector& _copy)


 {
{
 p=head;
p=head;
 _copy.p=_copy.head;
_copy.p=_copy.head;
 for(int i=0;i!=_copy.n;i++)
for(int i=0;i!=_copy.n;i++)


 {
{
 _copy.p=_copy.p->next;
_copy.p=_copy.p->next;
 p->extend_next(_copy.p->elem);
p->extend_next(_copy.p->elem);
 p=p->next;
p=p->next;


 }
}
 p->extend_next();
p->extend_next();
 n=_copy.n;
n=_copy.n;

 }
}
 int free()
int free()


 {
{
 for(int j=0;j!=n;j++)
for(int j=0;j!=n;j++)


 {
{
 head=head->next;
head=head->next;
 delete head->prev;
delete head->prev;
 }
}
 delete head->next;
delete head->next;
 delete head;
delete head;

 n=0;
n=0;
 p=0;
p=0;
 head=0;
head=0;
 return 1;
return 1;
 }
}
 ~vector()
~vector()


 {
{
 free();
free();
 }
}

 };
};

 };
};
 #endif
#endif