原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/hionceshine/archive/2008/11/19/3336318.aspx
Abstract
之前在(原創) 如何使用for_each() algorithm? (C/C++) (STL) 曾經討論過for_each(),不過當時功力尚淺,只談到了皮毛而已,這次看了effective STL的item 41、43後,對for_each()又有了更深入的了解,因此做了本篇心得報告。
Motivation
看到了eXile的C++中实现 foreach使用了巨集對foreach做改善,也看到了很多人對STL style的for_each()做討論,使我想對STL的for_each()再做了一次研究。
Introduction
學習過STL的container後,想要存取每一個iterator,你一定寫過以下的程式
 #include <vector>
#include <vector>
 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>

 using namespace std;
using namespace std;

 int main() {
int main() {
 int ia[] = {1, 2, 3};
int ia[] = {1, 2, 3};
 vector<int> ivec(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));
vector<int> ivec(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));

 for(vector<int>::const_iterator iter = ivec.begin(); iter != ivec.end(); ++iter) {
for(vector<int>::const_iterator iter = ivec.begin(); iter != ivec.end(); ++iter) {
 cout << *iter << endl;
cout << *iter << endl;
 }
}
 }
}
執行結果
當時我覺得STL什麼都好,就是以下這一串又臭又長
 for(vector<int>::const_iterator iter = ivec.begin(); iter != ivec.end(); ++iter) {
for(vector<int>::const_iterator iter = ivec.begin(); iter != ivec.end(); ++iter) {

若不常寫,一時還會寫不出來,其實若配合container,C++其實不應該這樣寫迴圈,正確的方式該使用for_each(),語法會變的相當簡單。
for_each()事實上是個function template,其實做如下[effective STL item 41]
 template<typename InputIterator, typename Function>
template<typename InputIterator, typename Function>
 Function for_each(InputIterator beg, InputIterator end, Function f) {
Function for_each(InputIterator beg, InputIterator end, Function f) {
 while(beg != end)
while(beg != end)
 f(*beg++);
f(*beg++);
 }
}

由以上source可知,for_each()只能配合global function和function object。
以下我們將對procedure based、object oriented、generics三種paradigm與for_each()搭配做探討。
Procedure Based與for_each()搭配
1.不傳入參數
1 /*
/*
2 (C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
(C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
3 Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_GlobalFunction.cpp
Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_GlobalFunction.cpp
4 Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
5 Description : Demo how to use for_each with global function
Description : Demo how to use for_each with global function
6 Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
7 */
*/
8 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
9 #include <vector>
#include <vector>
10 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
11 #include <algorithm>
#include <algorithm>
12
13 using namespace std;
using namespace std;
14
15 void printElem(int& elem) {
void printElem(int& elem) {
16 cout << elem << endl;
cout << elem << endl;
17 }
}
18
19 int main() {
int main() {
20 int ia[] = {1, 2, 3};
int ia[] = {1, 2, 3};
21 vector<int> ivec(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));
vector<int> ivec(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));
22
23 for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), printElem);
for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), printElem);
24 }
}
執行結果
23行
 for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), printElem);
for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), printElem);
只需將vector::begin(),vector::end()和global function name傳給for_each()即可,再也不用for迴圈那種複雜的語法了。
2.傳入參數
若要傳參數給global function,就不能再只傳global function name而已,必須透過ptr_fun()這個function adapter將global function轉成function object,然後再用bind2nd()將參數bind成一個function object。
1 /*
/*
2 (C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
(C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
3 Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_GlobalFunctionWithParameter.cpp
Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_GlobalFunctionWithParameter.cpp
4 Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
5 Description : Demo how to use for_each with global function with Parameter
Description : Demo how to use for_each with global function with Parameter
6 Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
7 */
*/
8 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
9 #include <vector>
#include <vector>
10 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
11 #include <algorithm>
#include <algorithm>
12 #include <functional>
#include <functional>
13
14 using namespace std;
using namespace std;
15
16 void printElem(int elem, const char* prefix) {
void printElem(int elem, const char* prefix) {
17 cout << prefix << elem << endl;
cout << prefix << elem << endl;
18 }
}
19
20 int main() {
int main() {
21 int ia[] = {1, 2, 3};
int ia[] = {1, 2, 3};
22 vector<int> ivec(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));
vector<int> ivec(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));
23
24 for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), bind2nd(ptr_fun(printElem), "Element:"));
for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), bind2nd(ptr_fun(printElem), "Element:"));
25 }
}
執行結果
 Element:1
Element:1
 Element:2
Element:2
 Element:3
Element:3
Object Oriented與for_each()搭配
1.不傳入參數
使用function object
1 /*
/*
2 (C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
(C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
3 Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_FunctionObject.cpp
Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_FunctionObject.cpp
4 Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
5 Description : Demo how to use for_each with function object
Description : Demo how to use for_each with function object
6 Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
7 */
*/
8 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
9 #include <vector>
#include <vector>
10 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
11 #include <algorithm>
#include <algorithm>
12
13 using namespace std;
using namespace std;
14
15 struct printElem {
struct printElem {
16 void operator() (int elem) {
void operator() (int elem) {
17 cout << elem << endl;
cout << elem << endl;
18 }
}
19 };
};
20
21 int main() {
int main() {
22 int ia[] = {1, 2, 3};
int ia[] = {1, 2, 3};
23 vector<int> ivec(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));
vector<int> ivec(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));
24
25 for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), printElem());
for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), printElem());
26 }
}
執行結果
2.傳入參數
若使用function object,也可以將參數傳給printElem(),透過constructor的技巧接收參數。
1 /*
/*
2 (C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
(C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
3 Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_FunctionObjectWithParameter.cpp
Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_FunctionObjectWithParameter.cpp
4 Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
5 Description : Demo how to use for_each with function object with parameter
Description : Demo how to use for_each with function object with parameter
6 Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
7 */
*/
8 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
9 #include <vector>
#include <vector>
10 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
11 #include <algorithm>
#include <algorithm>
12
13 using namespace std;
using namespace std;
14
15 struct printElem {
struct printElem {
16 const char* _prefix;
const char* _prefix;
17
18 printElem(const char* prefix) : _prefix(prefix) {}
printElem(const char* prefix) : _prefix(prefix) {}
19
20 void operator() (int elem) {
void operator() (int elem) {
21 cout << _prefix << elem << endl;
cout << _prefix << elem << endl;
22 }
}
23 };
};
24
25 int main() {
int main() {
26 int ia[] = {1, 2, 3};
int ia[] = {1, 2, 3};
27 vector<int> ivec(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));
vector<int> ivec(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));
28
29 for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), printElem("Element:"));
for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), printElem("Element:"));
30 }
}
執行結果
 Element:1
Element:1
 Element:2
Element:2
 Element:3
Element:3
function object有很多種寫法,但只要是function object都可以跟for_each()合作。
3.member_function與for_each()搭配
3.1 不傳入參數
本文的重點來了,在物件導向世界裡,最常用的就是for_each()配合member function,這該怎麼寫呢?直覺會這樣子寫
 for_each(_doorVec.begin(), _doorVec.end(),&Door::open);
for_each(_doorVec.begin(), _doorVec.end(),&Door::open);
由於global function name本身就是一個pointer,所以想藉由&Door::open傳進一個address,但這樣compile並不會過,正確解法是
 for_each(_doorVec.begin(), _doorVec.end(), mem_fun_ref(&Door::open));
for_each(_doorVec.begin(), _doorVec.end(), mem_fun_ref(&Door::open));
透過mem_fun_ref()這個function adapter將member function轉成function object。
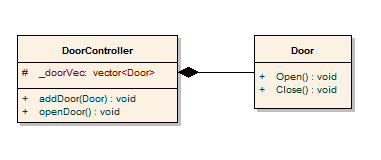
1 /*
/*
2 (C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
(C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
3
4 Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_MemberFunctionObject.cpp
Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_MemberFunctionObject.cpp
5 Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
6 Description : Demo how to use for_each with member function with object
Description : Demo how to use for_each with member function with object
7 Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
8 */
*/
9 #include <vector>
#include <vector>
10 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
11 #include <algorithm>
#include <algorithm>
12 #include <functional>
#include <functional>
13
14 using namespace std;
using namespace std;
15
16 class Door {
class Door {
17 public:
public:
18 void open() const {
void open() const {
19 cout << "open door horizontally" << endl;
cout << "open door horizontally" << endl;
20 }
}
21
22 void close() const {
void close() const {
23 cout << "close door horizontally" << endl;
cout << "close door horizontally" << endl;
24 }
}
25 };
};
26
27 class DoorController {
class DoorController {
28 protected:
protected:
29 vector<Door> _doorVec;
vector<Door> _doorVec;
30
31 public:
public:
32 void addDoor(Door aDoor) {
void addDoor(Door aDoor) {
33 _doorVec.push_back(aDoor);
_doorVec.push_back(aDoor);
34 }
}
35
36 void openDoor() const {
void openDoor() const {
37 for_each(_doorVec.begin(), _doorVec.end(), mem_fun_ref(&Door::open));
for_each(_doorVec.begin(), _doorVec.end(), mem_fun_ref(&Door::open));
38 }
}
39 };
};
40
41 int main() {
int main() {
42 DoorController dc;
DoorController dc;
43 dc.addDoor(Door());
dc.addDoor(Door());
44 dc.addDoor(Door());
dc.addDoor(Door());
45 dc.openDoor();
dc.openDoor();
46 }
}
執行結果
 open door horizontally
open door horizontally
 open door horizontally
open door horizontally
37行
 for_each(_doorVec.begin(), _doorVec.end(), mem_fun_ref(&Door::open));
for_each(_doorVec.begin(), _doorVec.end(), mem_fun_ref(&Door::open));
值得注意的是,mem_fun_ref()用在object的member function。若要搭配多型,vector必須放pointer,也就是得使用object pointer的member function,此時得使用mem_fun()將member function轉成function object。
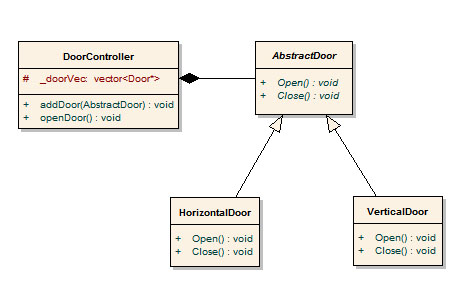
1 /*
/*
2 (C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
(C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
3
4 Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_MemberFunctionObjectPointer.cpp
Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_MemberFunctionObjectPointer.cpp
5 Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
6 Description : Demo how to use for_each with member function with object pointer
Description : Demo how to use for_each with member function with object pointer
7 Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
8 */
*/
9 #include <vector>
#include <vector>
10 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
11 #include <algorithm>
#include <algorithm>
12 #include <functional>
#include <functional>
13
14 using namespace std;
using namespace std;
15
16 class AbstractDoor {
class AbstractDoor {
17 public:
public:
18 virtual void open() const {
virtual void open() const {
19 cout << "open door horizontally" << endl;
cout << "open door horizontally" << endl;
20 }
}
21
22 virtual void close() const {
virtual void close() const {
23 cout << "close door horizontally" << endl;
cout << "close door horizontally" << endl;
24 }
}
25 };
};
26
27 class HorizontalDoor : public AbstractDoor {
class HorizontalDoor : public AbstractDoor {
28 };
};
29
30 class VerticalDoor : public AbstractDoor {
class VerticalDoor : public AbstractDoor {
31 public:
public:
32 void open() const {
void open() const {
33 cout << "open door vertically" << endl;
cout << "open door vertically" << endl;
34 }
}
35
36 void close() const {
void close() const {
37 cout << "close door vertically" << endl;
cout << "close door vertically" << endl;
38 }
}
39 };
};
40
41 class DoorController {
class DoorController {
42 protected:
protected:
43 vector<AbstractDoor*> _doorVec;
vector<AbstractDoor*> _doorVec;
44
45 public:
public:
46 void addDoor(AbstractDoor& aDoor) {
void addDoor(AbstractDoor& aDoor) {
47 _doorVec.push_back(&aDoor);
_doorVec.push_back(&aDoor);
48 }
}
49
50 void openDoor() const {
void openDoor() const {
51 for_each(_doorVec.begin(), _doorVec.end(), mem_fun(&AbstractDoor::open));
for_each(_doorVec.begin(), _doorVec.end(), mem_fun(&AbstractDoor::open));
52 }
}
53 };
};
54
55 int main() {
int main() {
56 DoorController dc;
DoorController dc;
57 dc.addDoor(HorizontalDoor());
dc.addDoor(HorizontalDoor());
58 dc.addDoor(VerticalDoor());
dc.addDoor(VerticalDoor());
59 dc.openDoor();
dc.openDoor();
60 }
}
執行結果
 open door horizontally
open door horizontally
 open door vertically
open door vertically
51行
 for_each(_doorVec.begin(), _doorVec.end(), mem_fun(&AbstractDoor::open));
for_each(_doorVec.begin(), _doorVec.end(), mem_fun(&AbstractDoor::open));
使用了mem_fun()。
3.2傳入參數
問題又來了,若要使member function也傳入參數呢?這時得使用bind2nd將function object和參數bind在一起,變成另外一個新的function object。
1 /*
/*
2 (C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
(C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
3
4 Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_MemberFunctionObjectPointerWithParameter.cpp
Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_MemberFunctionObjectPointerWithParameter.cpp
5 Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
6 Description : Demo how to use for_each with member function with object pointer
Description : Demo how to use for_each with member function with object pointer
7 Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
8 */
*/
9 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
10 #include <vector>
#include <vector>
11 #include <algorithm>
#include <algorithm>
12 #include <functional>
#include <functional>
13
14 using namespace std;
using namespace std;
15
16 class AbstractDoor {
class AbstractDoor {
17 public:
public:
18 virtual void open() const {
virtual void open() const {
19 cout << "open door horizontally" << endl;
cout << "open door horizontally" << endl;
20 }
}
21
22 virtual void close() const {
virtual void close() const {
23 cout << "close door horizontally" << endl;
cout << "close door horizontally" << endl;
24 }
}
25
26 virtual void openDoorBy(const char* name) const {
virtual void openDoorBy(const char* name) const {
27 cout << name << " ";
cout << name << " ";
28 open();
open();
29 }
}
30 };
};
31
32 class HorizontalDoor : public AbstractDoor {
class HorizontalDoor : public AbstractDoor {
33 };
};
34
35 class VerticalDoor : public AbstractDoor {
class VerticalDoor : public AbstractDoor {
36 public:
public:
37 void open() const {
void open() const {
38 cout << "open door vertically" << endl;
cout << "open door vertically" << endl;
39 }
}
40
41 void close() const {
void close() const {
42 cout << "close door vertically" << endl;
cout << "close door vertically" << endl;
43 }
}
44 };
};
45
46 class DoorController {
class DoorController {
47 protected:
protected:
48 vector<AbstractDoor*> _doorVec;
vector<AbstractDoor*> _doorVec;
49
50 public:
public:
51 void addDoor(AbstractDoor& aDoor) {
void addDoor(AbstractDoor& aDoor) {
52 _doorVec.push_back(&aDoor);
_doorVec.push_back(&aDoor);
53 }
}
54
55 void openDoor() const {
void openDoor() const {
56 for_each(_doorVec.begin(), _doorVec.end(), bind2nd(mem_fun(&AbstractDoor::openDoorBy), "John"));
for_each(_doorVec.begin(), _doorVec.end(), bind2nd(mem_fun(&AbstractDoor::openDoorBy), "John"));
57 }
}
58 };
};
59
60 int main() {
int main() {
61 DoorController dc;
DoorController dc;
62 dc.addDoor(HorizontalDoor());
dc.addDoor(HorizontalDoor());
63 dc.addDoor(VerticalDoor());
dc.addDoor(VerticalDoor());
64 dc.openDoor();
dc.openDoor();
65 }
}
執行結果
1 John open door horizontally
John open door horizontally
2 John open door vertically
John open door vertically
56行
 for_each(_doorVec.begin(), _doorVec.end(), bind2nd(mem_fun(&AbstractDoor::openDoorBy), "John"));
for_each(_doorVec.begin(), _doorVec.end(), bind2nd(mem_fun(&AbstractDoor::openDoorBy), "John"));
透過了bind2nd將參數結合後,成為一個新的function object。
Generics與for_each()搭配
1.Function Template
1.1不傳入參數
在泛型世界裡,那for_each()該怎麼配合function template呢?
1 /*
/*
2 (C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
(C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
3 Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_FunctionTemplate.cpp
Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_FunctionTemplate.cpp
4 Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
5 Description : Demo how to use for_each with function template
Description : Demo how to use for_each with function template
6 Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
7 */
*/
8 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
9 #include <vector>
#include <vector>
10 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
11 #include <algorithm>
#include <algorithm>
12
13 using namespace std;
using namespace std;
14
15 template<typename T>
template<typename T>
16 void printElem(T elem) {
void printElem(T elem) {
17 cout << elem << endl;
cout << elem << endl;
18 }
}
19
20 int main() {
int main() {
21 int ia[] = {1, 2, 3};
int ia[] = {1, 2, 3};
22 vector<int> ivec(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));
vector<int> ivec(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));
23
24 for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), printElem<int>);
for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), printElem<int>);
25 //for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), (void(*)(int))printElem);
//for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), (void(*)(int))printElem);
26 }
}
執行結果
若使用function template,有兩種寫法
一種是
 for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), printElem<int>);
for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), printElem<int>);
由於template function需要在compile時確定型別,所以要加上<int>確定為int型別。
另外一種寫法
 for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), (void(*)(int))printElem);
for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), (void(*)(int))printElem);
template function並沒有確定型別,但轉成function pointer時,並須明確轉成int型別的function pointer。
1.2 傳入參數
若要如function object那樣能傳參數呢?funtion template是可以,不過有些限制,若使用nontype parameter,只能使用以下三種型別
1.int或enum
2.pointer:pointer to object,pointer to function,pointer to member。
3.reference:reference to object,reference to function。
1 /*
/*
2 (C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
(C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
3 Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_FunctionTemplateWithNontypeParameter.cpp
Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_FunctionTemplateWithNontypeParameter.cpp
4 Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
5 Description : Demo how to use for_each with function template with nontype parameter
Description : Demo how to use for_each with function template with nontype parameter
6 Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
7 */
*/
8 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
9 #include <vector>
#include <vector>
10 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
11 #include <algorithm>
#include <algorithm>
12
13 using namespace std;
using namespace std;
14
15 template<typename T, int i>
template<typename T, int i>
16 void printElem(T elem) {
void printElem(T elem) {
17 cout << i << ":" << elem << endl;
cout << i << ":" << elem << endl;
18 }
}
19
20 int main() {
int main() {
21 int ia[] = {1, 2, 3};
int ia[] = {1, 2, 3};
22 vector<int> ivec(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));
vector<int> ivec(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));
23
24 for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), printElem<int, 5>);
for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), printElem<int, 5>);
25 }
}
執行結果
所以無法如function object那樣可以傳入字串或任意型別,最少在目前ISO C++標準是做不到的。
既然討論了function template,那最具威力的class template是否也能搭配for_each()?
2.Class Template
2.1 不傳入參數
1 /*
/*
2 (C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
(C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
3 Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_ClassTemplate.cpp
Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_ClassTemplate.cpp
4 Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
5 Description : Demo how to use for_each with class template
Description : Demo how to use for_each with class template
6 Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
7 */
*/
8 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
9 #include <vector>
#include <vector>
10 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
11 #include <algorithm>
#include <algorithm>
12 #include <functional>
#include <functional>
13
14 using namespace std;
using namespace std;
15
16 template<typename T>
template<typename T>
17 class printElem : public unary_function<T, void> {
class printElem : public unary_function<T, void> {
18 public:
public:
19 void operator() (T elem) {
void operator() (T elem) {
20 cout << elem << endl;
cout << elem << endl;
21 }
}
22 };
};
23
24 int main() {
int main() {
25 int ia[] = {1, 2, 3};
int ia[] = {1, 2, 3};
26 vector<int> ivec(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));
vector<int> ivec(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));
27
28 for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), printElem<int>());
for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), printElem<int>());
29 }
}
執行結果
17行
 class printElem : public unary_function<T, void> {
class printElem : public unary_function<T, void> {
因為printElem只接受for_each()所傳的參數,算是單參數而已,所以public繼承了unary_function<T,void>,因為for_each的定義
 template <class InputIterator, class UnaryFunction>
template <class InputIterator, class UnaryFunction>
 UnaryFunction for_each(InputIterator first, InputIterator last, UnaryFunction f);
UnaryFunction for_each(InputIterator first, InputIterator last, UnaryFunction f);
傳進去的是UnaryFunction型別,第一個type parameter T表示傳入的型別,第二個type parameter void,表示回傳的型別,最後重新定義operator()。
2.2 傳入參數
若要使class template也能傳入參數,一樣利用function object的技巧,借用constructor。
1 /*
/*
2 (C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
(C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
3 Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_ClassTemplateWithParameter.cpp
Filename : GenericAlgo_for_each_ClassTemplateWithParameter.cpp
4 Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / BCB 6.0 / gcc 3.4.2 / ISO C++
5 Description : Demo how to use for_each with class template & parameter
Description : Demo how to use for_each with class template & parameter
6 Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
Release : 05/11/2007 1.0
7 */
*/
8 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
9 #include <vector>
#include <vector>
10 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
11 #include <algorithm>
#include <algorithm>
12 #include <functional>
#include <functional>
13
14 using namespace std;
using namespace std;
15
16 template<typename T, typename U>
template<typename T, typename U>
17 class printElem : public unary_function<T, void> {
class printElem : public unary_function<T, void> {
18 private:
private:
19 U _prefix;
U _prefix;
20
21 public:
public:
22 printElem(U prefix) : _prefix(prefix) {}
printElem(U prefix) : _prefix(prefix) {}
23
24 void operator() (T elem) {
void operator() (T elem) {
25 cout << _prefix << elem << endl;
cout << _prefix << elem << endl;
26 }
}
27 };
};
28
29 int main() {
int main() {
30 int ia[] = {1, 2, 3};
int ia[] = {1, 2, 3};
31 vector<int> ivec(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));
vector<int> ivec(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));
32
33 for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), printElem<int, const char*>("Element:"));
for_each(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), printElem<int, const char*>("Element:"));
34 }
}
執行結果
 Element:1
Element:1
 Element:2
Element:2
 Element:3
Element:3
Conclusion
STL的for_each()事實上很好用,不過由於限制很多,所以常令很多新手卻步,本文試著將所有會遇到問題的地方都提出來討論,包括procedure based、object oriented、generics三種paradigm與for_each()的搭配都涵蓋了,希望對各位有幫助。
posted on 2011-04-18 13:11
风轻云淡 阅读(35592)
评论(3) 编辑 收藏 引用 所属分类:
C++