1. 遗传算法的数据结构大致画了下数据结构的逻辑图,如下:
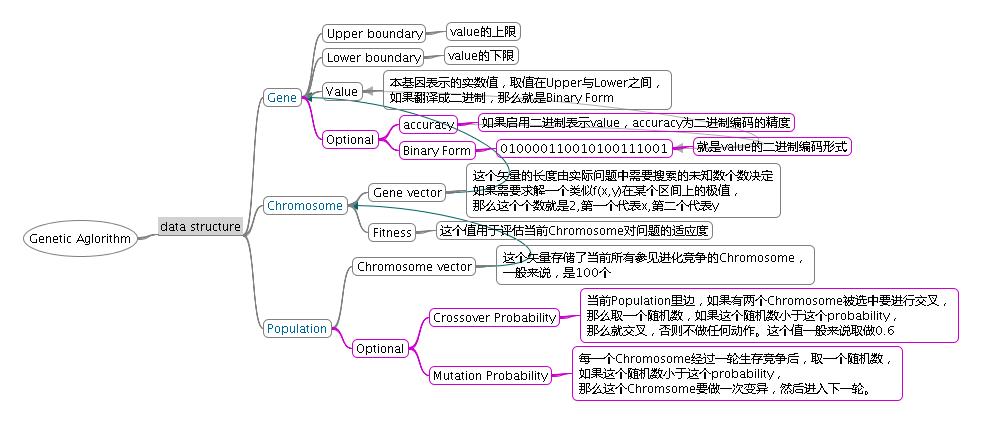
参加生存竞争的整个群体称为种群(Population),种群中所有参与进化的个体(Chromosome)的数量一般为一个定值,而每个个体可能含有多于一个基因(Gene)。
例如,求解一个Camel函数在区间-100<x,y<100上边的最小值:
f(x,y)=[4 - 2.1(x^2) + (x^3)/3](x^2) + xy +[-4 +4(y^2)](y^2)
这时候就需要两个基因,每个基因上限是100,下限是-100.
假设数值求解的精度为10^(-7),那么对应的二进制编码长度N可以这样确定
(2^N)-1 >= [ 100 - ( -100 ) ] / [ 10^(-7) ]
于是,将一个十进制数字x转化为二进制
x' = [x- (-100)] * [(2^N) -1] / [ 100 - ( -100 ) ]
同样,也可以将一个二进制数字x'转化为十进制数字x
程序中,数据结构可以这样定义
1 struct Gene
2 {
3 long double Upper; //upper boundary of the value
4 long double Lower; //lower boundary of the value
5 long double Value; //decimal value of the gene
6 std :: vector< int > Binary_Array; //binary form of the value
7 long double Accuracy; //accuracy of the value
8 };
9
10 struct Chromosome
11 {
12 std :: vector< Gene > Gene_Array; //Gene[]
13 long double Fitness; //the weigh of the chromosome in ga
14 };
15
16 struct Population
17 {
18 std :: vector< Chromosome > Chromosome_Array; //Chromosome[]
19
20 long double Mutation_Probability; //probability of mutation
21 long double Crossover_Probability; //probability of crossover
22 };
2. 与数据结构相关的基本算法1) 基因的自动初始化 --在搜索区间中随机生成初始基因
1 //generate random value
2 void initialize( Gene& g)
3 {
4 const long double Ran = ran();
5 const long double Upper = g.Upper;
6 const long double Lower = g.Lower;
7 //const long double Accuracy = g.Accuracy;
8 assert( Upper > Lower );
9
10 g.Value = Lower + Ran * ( Upper - Lower );
11 }
12
2) 基因的二进制编码--将十进制数据编码为二进制
1 //decimal value -> binary form
2 void encoding( Gene& g )
3 {
4 const long double Value = g.Value;
5 const long double Upper = g.Upper;
6 const long double Lower = g.Lower;
7 const long double Accuracy = g.Accuracy;
8
9 unsigned int Size = 1 +
10 static_cast< unsigned int >
11 (
12 log( ( Upper - Lower ) / ( Accuracy ) ) /
13 log( 2.0 )
14 );
15
16 if ( Size > 63 )
17 Size = 63;
18
19 const unsigned long long Max = 1 << Size;
20
21 unsigned long long x =
22 static_cast< unsigned long long >
23 (
24 static_cast< long double>( Max -1 ) *
25 ( Value - Lower ) /
26 ( Upper - Lower )
27 );
28
29 std :: vector<int> Binary_Array;
30
31 for ( unsigned int i = 0; i <= Size; ++i )
32 {
33 if ( x & 1 ) //case odd
34 {
35 Binary_Array.push_back( 1 );
36 }
37 else //case even
38 {
39 Binary_Array.push_back( 0 );
40 }
41 x >>= 1;
42 }
43
44 g.Binary_Array = Binary_Array;
45
46 }
47
3)二进制向十进制的解码--将二进制数据解码为十进制
1 //binary form -> decimal value
2 void decoding( Gene& g )
3 {
4 const unsigned int Size = g.Binary_Array.size();
5 assert( Size > 0 );
6
7 const long double Upper = g.Upper;
8 const long double Lower = g.Lower;
9 //const long double Accuracy = g.Accuracy;
10 const std::vector<int> Binary_Array = g.Binary_Array;
11
12 const unsigned long long Max = 1 << Size;
13 unsigned long long x = 0;
14
15 for( unsigned int i = Size; i > 0; --i )
16 {
17 x += Binary_Array[i-1];
18 x <<= 1;
19 }
20 //x += Binary_Array[0];
21
22 const long double Value = Lower +
23 static_cast<long double>( x ) /
24 static_cast<long double>( Max - 1 ) *
25 ( Upper - Lower );
26
27 g.Value = Value;
28 }
4)普通二进制编码转到格雷码
多说一点,在进行二进制交叉的时候,使用格雷码比普通的二进制编码要有效一点。
例如,如果采用普通二进制编码,8可以表示为1000,而7则表示为0111,四个位都是不同的,7与8仅仅相差了1,但是普通二进制编码却相差了这么多,如果对他们进行交叉的话,出来的结果偏离7与8实在太远了,而使用格雷码则可以避免这种尴尬。
这里(http://baike.baidu.com/view/358724.htm)是百度一个有关格雷码的介绍,我就不复制了,有兴趣的话过去看看。
1 //Normal Binary Form --> Gray Binary Form
2 void normal2gray( Gene& g )
3 {
4 const unsigned int Size = g.Binary_Array.size();
5 assert( Size > 0 );
6
7 std :: vector<int> G_Binary_Array; //gray code
8 const std :: vector<int> Binary_Array = g.Binary_Array;
9
10 G_Binary_Array.push_back( Binary_Array[0] );
11 for ( unsigned int i = 1; i < Size; ++i )
12 {
13 G_Binary_Array.push_back( ( Binary_Array[i-1] + Binary_Array[i] ) & 1 );
14 }
15 g.Binary_Array = G_Binary_Array;
16 }
17
5) 格雷码转换到普通二进制编码
1 //Gray Binary Form --> Normal Binary Form
2 void normal2binary( Gene& g )
3 {
4 const unsigned int Size = g.Binary_Array.size();
5 assert( Size > 0 );
6
7 std :: vector<int> N_Binary_Array; //Normal Binary Form
8 const std :: vector<int> Binary_Array = g.Binary_Array;
9
10 unsigned int result = 0;
11 for ( unsigned int i = 0; i < Size; ++i )
12 {
13 result += Binary_Array[i];
14 N_Binary_Array.push_back( result & 1 );
15 }
16
17 g.Binary_Array = N_Binary_Array;
18 }
19
20
6) 进化种群初始化函数一 -- 生成进化个体
1 void initialize( Population& population,
2 const unsigned int size
3 )
4 {
5 Chromosome* chromosome = new Chromosome;
6
7 population.Generation = 1;
8
9 for ( unsigned int i = 0; i < size; ++i )
10 {
11
12 population.Chromosome_Array.push_back( *chromosome );
13 }
14
15 delete chromosome;
16 }
17
7) 进化种群初始化函数二 -- 对种群中的每个个体,初始化其基因
如上边的Camel函数,因为里边有两个自变量需要搜索,那么需要调用这个函数两次,分别对应于x和y
append_gene( p, 100, -100, 1E-7);
append_gene( p, 100, -100, 1E-7);
1 void append_gene( Population& population,
2 const long double& upper,
3 const long double& lower,
4 const long double& accuracy
5 )
6 {
7 assert( upper > lower );
8 assert( accuracy > 0 );
9
10 Gene* gene = new Gene;
11
12 gene -> Upper = upper;
13 gene -> Lower = lower;
14 gene -> Accuracy = accuracy;
15
16 const unsigned int Size = population.Chromosome_Array.size();
17 for ( unsigned int i = 0; i < Size; ++i )
18 {
19 initialize( *gene );
20 population.Chromosome_Array[i].Gene_Array.push_back( *gene );
21 }
22
23 delete gene;
24 }
25
8) 搜寻最佳适应度个体 -- 进化到指定年代后,找出最佳个体
1 const std :: vector< long double > elite( const Population& population )
2 {
3 const unsigned int Size = population.Chromosome_Array.size();
4 assert( Size > 0 );
5 long double max = population.Chromosome_Array[0].Fitness;
6 unsigned int index = 0;
7 for ( unsigned int i = 1; i < Size; ++i )
8 {
9 if ( population.Chromosome_Array[i].Fitness > max )
10 {
11 index = i;
12 max = population.Chromosome_Array[i].Fitness;
13 }
14 }
15
16 std :: vector<long double> Elite;
17 const unsigned int G_Size = population.Chromosome_Array[0].Gene_Array.size();
18 for ( unsigned int i = 0; i < G_Size; ++i )
19 Elite.push_back( population.Chromosome_Array[index].Gene_Array[i].Value );
20
21 return Elite;
22 }
9) 随机函数
由于遗传算法是一种随机搜索算法,执行的时候需要大量的随机数(记得之前搜索四个未知数,种群100个体,进化800代,大概整个运行过程用了10^10数量级的随机数),库里的随机数生成函数肯定不行。当前使用了一个Kruth推荐的(Kruth, D. E. 1997, Seminumerical Algorithms, vol2. $3)、基于相减方法的随机数生成算法,比基于线性同余方法的快一点。
1 #include <ctime>
2
3 static long double _ran( int& seed );
4
5 long double ran()
6 {
7 static int seed = static_cast < unsigned int >( time( NULL ) );
8 return _ran( seed );
9 }
10
11 static long double _ran( int& seed )
12 {
13
14 const int MBIG = 1000000000;
15 const int MSEED = 161803398;
16 const int MZ = 0;
17 const long double FAC = 1.0E-9L;
18
19 static int inext, inextp;
20 static long ma[56];
21 static int iff = 0;
22 long mj, mk;
23 int i, ii, k;
24
25 if ( seed < 0 || iff == 0)
26 {
27 iff = 1;
28 mj = MSEED - (seed < 0 ? -seed : seed);
29 mj %= MBIG;
30 ma[55] = mj;
31 mk = 1;
32 for (i = 1; i <= 54; i++) {
33 ii = (21 * i) % 55;
34 ma[ii] = mk;
35 mk = mj - mk;
36 if (mk < MZ)
37 mk += MBIG;
38 mj = ma[ii];
39 }
40 for (k = 1; k <= 4; k++)
41 for (i = 1; i <= 55; i++)
42 {
43 ma[i] -= ma[1 + (i + 30) % 55];
44 if (ma[i] < MZ)
45 ma[i] += MBIG;
46 }
47 inext = 0;
48 inextp = 31;
49 seed = 1;
50 }
51 if (++inext == 56)
52 inext = 1;
53 if (++inextp == 56)
54 inextp = 1;
55 mj = ma[inext] - ma[inextp];
56 if (mj < MZ)
57 mj += MBIG;
58 ma[inext] = mj;
59 return mj * FAC;
60 }
61
62
posted on 2008-06-16 16:53
Wang Feng 阅读(2974)
评论(0) 编辑 收藏 引用 所属分类:
Numerical C++