之前有借助于 STL 中的 multimap 实现查找最小的 k 个元素。
这里继续解决 查找最小的 k 个元素,采用 最大根堆。
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <ctime>
3 #include <vector>
4 using namespace std;
5
6 class Heap
7 {
8 private:
9 int* data;
10 int _size;
11 int _capacity;
12 public:
13 Heap()
14 {
15 _size = 0;
16 _capacity = 2 * _size;
17 data = new int[_capacity];
18 if (data == 0)
19 {
20 exit(1);
21 }
22 }
23 Heap(const Heap& h)
24 {
25 _size = h._size;
26 _capacity = h._capacity;
27 data = new int[_capacity];
28 if (data == 0)
29 {
30 exit(1);
31 }
32 memcpy(data, h.data, sizeof (int) * h._size);
33 }
34 Heap& operator =(const Heap& h)
35 {
36 delete [] data;
37 _size = h._size;
38 _capacity = h._capacity;
39 data = new int[_capacity];
40 if (data == 0)
41 {
42 exit(1);
43 }
44 memcpy(data, h.data, sizeof (int) * h._size);
45 }
46 ~Heap()
47 {
48 delete [] data;
49 }
50 void insert(int item)
51 {
52 if (_size >= _capacity - 1)
53 {
54 _capacity = (_capacity + 1) * 2;
55 int * tmp = new int[_capacity];
56 if (tmp == 0)
57 {
58 exit(1);
59 }
60 // 1
61 memcpy(tmp, data, sizeof (int) * _capacity / 2 - 1);
62 delete [] data;
63 data = tmp;
64 }
65 data[++_size] = item;
66 int pos1 = _size;
67 int pos2 = pos1 / 2;
68 while (pos2 >= 1 && data[pos1] > data[pos2])
69 {
70 data[pos1] ^= data[pos2];
71 data[pos2] ^= data[pos1];
72 data[pos1] ^= data[pos2];
73 pos1 = pos2;
74 pos2 = pos1 / 2;
75 }
76 }
77 int max()
78 {
79 return data[1];
80 }
81 int erase()
82 {
83 int tmp = data[1];
84 data[1] = data[_size];
85 --_size;
86 int pos1 = 1, pos2;
87 pos2 = pos1 * 2;
88
89 while (pos2 <= _size)
90 {
91 if (pos2 < _size && data[pos2 + 1] > data[pos2])
92 {
93 ++pos2;
94 }
95 if (data[pos1] < data[pos2])
96 {
97 data[pos1] ^= data[pos2];
98 data[pos2] ^= data[pos1];
99 data[pos1] ^= data[pos2];
100 }
101 pos1 = pos2;
102 pos2 = pos1 * 2;
103 }
104 return tmp;
105 }
106 int size()
107 {
108 return _size;
109 }
110 int capacity()
111 {
112 return _capacity;
113 }
114 void test()
115 {
116 for (int i = 1; i <= _size; ++i)
117 {
118 cout << data[i] << ' ';
119 }
120 cout << endl;
121 }
122 };
123
124 void findMinK(Heap& h, int k, const vector<int>& data)
125 {
126 int m = 0;
127 for (vector<int>::const_iterator cit = data.begin(); cit != data.end(); ++cit)
128 {
129 if (m < k)
130 {
131 h.insert(*cit);
132 ++m;
133 }
134 else
135 {
136 if (*cit < h.max())
137 {
138 h.erase();
139 h.insert(*cit);
140 }
141 }
142 }
143 }
144
145 int main()
146 {
147 int n = 100;
148 Heap h;
149 vector<int> data;
150 srand(time(0));
151 while (n--)
152 {
153 data.push_back(rand());
154 }
155 findMinK(h, 10, data);
156 for (vector<int>::const_iterator cit = data.begin(); cit != data.end(); ++cit)
157 {
158 cout << *cit << ' ';
159 }
160 cout << endl;
161 for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
162 {
163 cout << h.erase() << endl;
164 }
165 cout << endl;
166 return 0;
167 }
posted @
2011-04-27 00:03 unixfy 阅读(255) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
一个简单的堆的实现,大根堆。
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <ctime>
3 using namespace std;
4
5 class Heap
6 {
7 private:
8 int* data;
9 int _size;
10 int _capacity;
11 public:
12 Heap()
13 {
14 _size = 0;
15 _capacity = 2 * _size;
16 data = new int[_capacity];
17 if (data == 0)
18 {
19 exit(1);
20 }
21 }
22 Heap(const Heap& h)
23 {
24 _size = h._size;
25 _capacity = h._capacity;
26 data = new int[_capacity];
27 if (data == 0)
28 {
29 exit(1);
30 }
31 memcpy(data, h.data, sizeof (int) * h._size);
32 }
33 Heap& operator =(const Heap& h)
34 {
35 delete [] data;
36 _size = h._size;
37 _capacity = h._capacity;
38 data = new int[_capacity];
39 if (data == 0)
40 {
41 exit(1);
42 }
43 memcpy(data, h.data, sizeof (int) * h._size);
44 }
45 ~Heap()
46 {
47 delete [] data;
48 }
49 void insert(int item)
50 {
51 if (_size >= _capacity - 1)
52 {
53 _capacity = (_capacity + 1) * 2;
54 int * tmp = new int[_capacity];
55 if (tmp == 0)
56 {
57 exit(1);
58 }
59 // 1
60 memcpy(tmp, data, sizeof (int) * _capacity / 2 - 1);
61 delete [] data;
62 data = tmp;
63 }
64 data[++_size] = item;
65 int pos1 = _size;
66 int pos2 = pos1 / 2;
67 while (pos2 >= 1 && data[pos1] > data[pos2])
68 {
69 data[pos1] ^= data[pos2];
70 data[pos2] ^= data[pos1];
71 data[pos1] ^= data[pos2];
72 pos1 = pos2;
73 pos2 = pos1 / 2;
74 }
75 }
76 int max()
77 {
78 return data[1];
79 }
80 int erase()
81 {
82 int tmp = data[1];
83 data[1] = data[_size];
84 --_size;
85 int pos1 = 1, pos2;
86 pos2 = pos1 * 2;
87
88 while (pos2 <= _size)
89 {
90 if (pos2 < _size && data[pos2 + 1] > data[pos2])
91 {
92 ++pos2;
93 }
94 if (data[pos1] < data[pos2])
95 {
96 data[pos1] ^= data[pos2];
97 data[pos2] ^= data[pos1];
98 data[pos1] ^= data[pos2];
99 }
100 pos1 = pos2;
101 pos2 = pos1 * 2;
102 }
103 return tmp;
104 }
105 int size()
106 {
107 return _size;
108 }
109 int capacity()
110 {
111 return _capacity;
112 }
113 void test()
114 {
115 for (int i = 1; i <= _size; ++i)
116 {
117 cout << data[i] << ' ';
118 }
119 cout << endl;
120 }
121 };
122
123 int main()
124 {
125 int n = 10;
126 Heap h;
127 srand(time(0));
128 while (n--)
129 // for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
130 {
131 h.insert(rand());
132 // h.insert(i);
133 // cout << h.size() << ' ' << h.capacity() << endl;
134 }
135 h.test();
136 for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
137 {
138 cout << h.erase() << endl;
139 }
140 h.test();
141 return 0;
142 }
posted @
2011-04-26 23:54 unixfy 阅读(172) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏直观的解法是对所有的 N 个数进行排序,再取最前或最后的 k 个元素。
这种做法的时间复杂度为 O(NlogN) 。
一种较好的解法是:维持一个 k 个元素的集合 S,遍历 N 个数,对每个元素,首先检查 S 中的元素个数是否小于 k,如果小于直接加入到 S 中。如果 S 中已有 k 个元素,则比较待处理元素与 S 中最大的元素的大小关系,若小于 S 中最大的元素,则删除 S 中最大的元素,并将该元素加入到 S 中。
怎样才能快速地从 S 中寻找到我们想要的最大的元素,使用堆是个好方法,最大堆。每次直接去堆的第一个元素即是 S 中最大的元素。如果将 S 中的最大元素删除,然后将 最后的一个元素放在堆顶,下滑,已调整堆。在讲新的元素加入到堆中,上滑,以调整堆。可以将这两个过程合并,即将 S 中最大的元素替换为 待处理的元素。对这个堆顶上的元素下滑,以调整堆。这里的复杂度为 O(Nlogk)。
STL 中的 multimap 不是堆,但是其可以以 O(logn) 维护其有序性,所以可以直接用 multimap 代替堆来实现。
http://zhedahht.blog.163.com/blog/static/2541117420072432136859/
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <vector>
3 #include <set>
4 #include <ctime>
5 using namespace std;
6
7 void findMinK(multiset<int, greater<int> >& Kdata, int k, const vector<int>& data)
8 {
9 Kdata.clear();
10 int m = 0;
11 for (vector<int>::const_iterator cit = data.begin(); cit != data.end(); ++cit)
12 {
13 if (m < k)
14 {
15 Kdata.insert(*cit);
16 ++m;
17 }
18 else
19 {
20 if (*cit < *(Kdata.begin()))
21 {
22 Kdata.erase(Kdata.begin());
23 Kdata.insert(*cit);
24 }
25 }
26 }
27 }
28
29 int main()
30 {
31 vector<int> data;
32 srand(time(0));
33 int n = 100;
34 while (n--)
35 {
36 data.push_back(rand());
37 }
38 multiset<int, greater<int> > Kdata;
39 findMinK(Kdata, 10, data);
40 for (vector<int>::const_iterator cit = data.begin(); cit != data.end(); ++cit)
41 {
42 cout << *cit << ' ';
43 }
44 cout << endl;
45 for (multiset<int, greater<int> >::const_iterator cit = Kdata.begin(); cit != Kdata.end(); ++cit)
46 {
47 cout << *cit << ' ';
48 }
49 cout << endl;
50 return 0;
51 }
posted @
2011-04-26 22:59 unixfy 阅读(1223) |
评论 (3) |
编辑 收藏
来自于《大话设计模式》
观察者模式:定义了一种一对多的依赖关系,让多个观察者对象同时监听某一个主题对象。这个主题对象在状态发生时,会通知所有观察者对象,使他们自动更新自己。
行为型模式。
UML 类图:
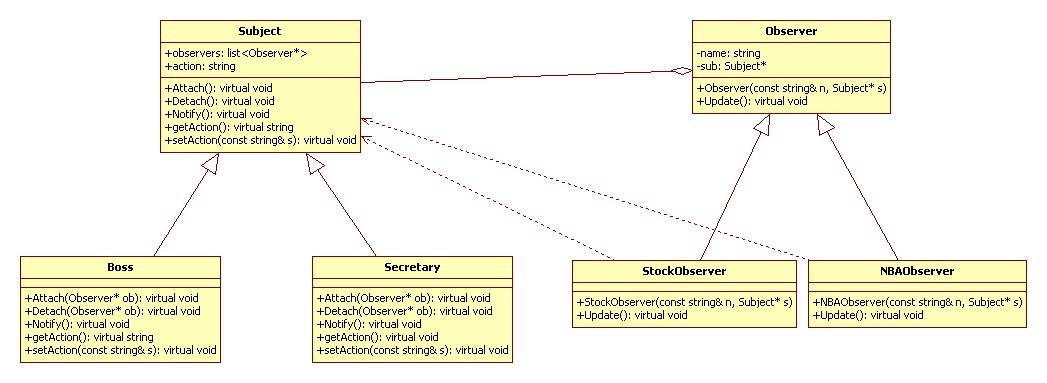
代码实现 C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string>
3 #include <list>
4 #include <algorithm>
5 using namespace std;
6
7 class Subject;
8
9 class Observer
10 {
11 protected:
12 string name;
13 Subject* sub;
14 public:
15 Observer(const string& n, Subject* s) : name(n), sub(s) {}
16 virtual void Update() = 0;
17 };
18
19 class Subject
20 {
21 protected:
22 list<Observer*> observers;
23 string action;
24 public:
25 virtual void Attach(Observer* ob) = 0;
26 virtual void Detach(Observer* ob) = 0;
27 virtual void Notify() = 0;
28 virtual void setAction(const string& s) = 0;
29 virtual string getAction() = 0;
30 };
31
32 class StockObserver : public Observer
33 {
34 public:
35 StockObserver(const string& name, Subject* s) : Observer(name, s) {}
36 virtual void Update()
37 {
38 cout << sub->getAction() << '\t' << name << " 关闭股票行情,继续工作!" << endl;
39 }
40 };
41
42 class NBAObserver : public Observer
43 {
44 public:
45 NBAObserver(const string& name, Subject* s) : Observer(name, s) {}
46 virtual void Update()
47 {
48 cout << sub->getAction() << '\t' << name << " 关闭 NBA,继续工作!" << endl;
49 }
50 };
51
52 class Boss : public Subject
53 {
54 //private:
55 // list<Observer*> observers;
56 // string action;
57 public:
58 virtual void Attach(Observer* ob)
59 {
60 observers.push_back(ob);
61 }
62 virtual void Detach(Observer* ob)
63 {
64 list<Observer*>::iterator iter= find(observers.begin(), observers.end(), ob);
65 if (iter != observers.end())
66 {
67 observers.erase(iter);
68 }
69 }
70 virtual void Notify()
71 {
72 for (list<Observer*>::iterator iter = observers.begin(); iter != observers.end(); ++iter)
73 {
74 (*iter)->Update();
75 }
76 }
77 virtual void setAction(const string& s)
78 {
79 action = s;
80 }
81 virtual string getAction()
82 {
83 return action;
84 }
85 };
86
87 class Secretary : public Subject
88 {
89 //private:
90 // list<Observer*> observers;
91 // string action;
92 public:
93 virtual void Attach(Observer* ob)
94 {
95 observers.push_back(ob);
96 }
97 virtual void Detach(Observer* ob)
98 {
99 list<Observer*>::iterator iter = find(observers.begin(), observers.end(), ob);
100 if (iter != observers.end())
101 {
102 observers.erase(iter);
103 }
104 }
105 virtual void Notify()
106 {
107 for (list<Observer*>::iterator iter = observers.begin(); iter != observers.end(); ++iter)
108 {
109 (*iter)->Update();
110 }
111 }
112 virtual void setAction(const string& s)
113 {
114 action = s;
115 }
116 virtual string getAction()
117 {
118 return action;
119 }
120 };
121
122
123
124 int main()
125 {
126 Boss* huhansan = new Boss;
127 StockObserver* so = new StockObserver("abc", huhansan);
128 NBAObserver* no = new NBAObserver("xyz", huhansan);
129
130 huhansan->Attach(so);
131 huhansan->Attach(no);
132 huhansan->setAction("我胡汉三又回来了!");
133 huhansan->Notify();
134
135 huhansan->Detach(no);
136 huhansan->setAction("开会!");
137 huhansan->Notify();
138
139 delete huhansan;
140
141 Secretary* s = new Secretary;
142 s->Attach(no);
143 s->Attach(so);
144 s->setAction("老板来了!");
145 cout << s->getAction() << endl;
146 s->Notify();
147
148 delete so;
149 delete no;
150 delete s;
151
152 return 0;
153 }
posted @
2011-04-26 19:28 unixfy 阅读(317) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
来自于《大话设计模式》
建造者模式(Builder):将一个复杂对象的构建与它的表示分离,使得同样的构建过程可以创建不同的表示。
UML 类图:
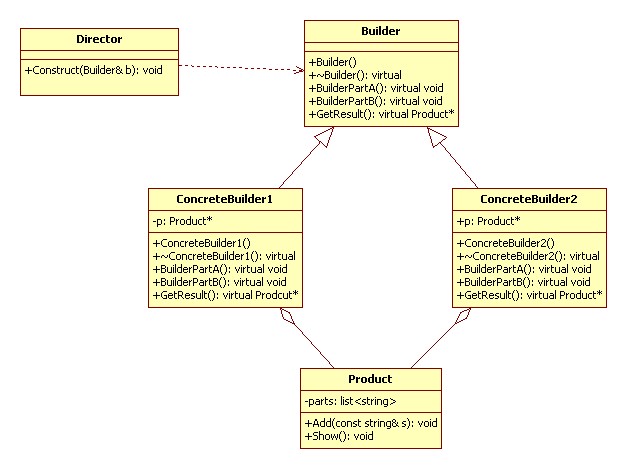
代码实现 C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string>
3 #include <list>
4 using namespace std;
5
6 class Product
7 {
8 private:
9 list<string> parts;
10 public:
11 void Add(string s)
12 {
13 parts.push_back(s);
14 }
15 void Show()
16 {
17 for (list<string>::const_iterator cit = parts.begin(); cit != parts.end(); ++cit)
18 {
19 cout << *cit << endl;
20 }
21 }
22 };
23
24 class Builder
25 {
26 public:
27 Builder() {}
28 virtual ~Builder() {}
29 virtual void BuildPartA() = 0;
30 virtual void BuildPartB() = 0;
31 virtual Product* GetResult() = 0;
32 };
33
34 class ConcreteBuilder1 : public Builder
35 {
36 private:
37 Product* p;
38 public:
39 ConcreteBuilder1() : p(new Product) {}
40 virtual ~ConcreteBuilder1()
41 {
42 delete p;
43 }
44 virtual void BuildPartA()
45 {
46 p->Add("部件 A - 1");
47 }
48 virtual void BuildPartB()
49 {
50 p->Add("部件 B - 1");
51 }
52 virtual Product* GetResult()
53 {
54 return p;
55 }
56 };
57
58 class ConcreteBuilder2 : public Builder
59 {
60 private:
61 Product* p;
62 public:
63 ConcreteBuilder2() : p(new Product) {}
64 virtual ~ConcreteBuilder2()
65 {
66 delete p;
67 }
68 virtual void BuildPartA()
69 {
70 p->Add("部件 A - 2");
71 }
72 virtual void BuildPartB()
73 {
74 p->Add("部件 B - 2");
75 }
76 virtual Product* GetResult()
77 {
78 return p;
79 }
80 };
81
82 class Director
83 {
84 public:
85 void Construct(Builder& b)
86 {
87 b.BuildPartA();
88 b.BuildPartB();
89 }
90 };
91
92 int main()
93 {
94 Director d;
95 ConcreteBuilder1 b1;
96 ConcreteBuilder2 b2;
97
98 d.Construct(b1);
99 Product* p1 = b1.GetResult();
100 p1->Show();
101
102 d.Construct(b2);
103 Product* p2 = b2.GetResult();
104 p2->Show();
105
106 return 0;
107 }
posted @
2011-04-26 18:00 unixfy 阅读(265) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
来自于《大话设计模式》
外观模式(Facade):为子系统的一组接口提供一个一致的界面,此模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更加容易使用。
UML 类图:
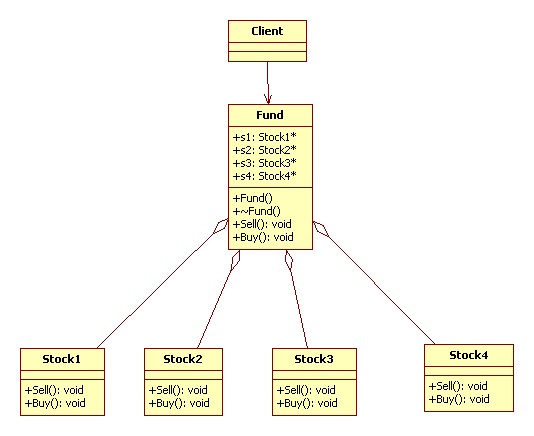
代码实现 C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 class Stock1
5 {
6 public:
7 void Sell()
8 {
9 cout << "股票 1 卖出" << endl;
10 }
11 void Buy()
12 {
13 cout << "股票 1 买入" << endl;
14 }
15 };
16
17 class Stock2
18 {
19 public:
20 void Sell()
21 {
22 cout << "股票 2 卖出" << endl;
23 }
24 void Buy()
25 {
26 cout << "股票 2 买入" << endl;
27 }
28 };
29
30 class Stock3
31 {
32 public:
33 void Sell()
34 {
35 cout << "股票 3 卖出" << endl;
36 }
37 void Buy()
38 {
39 cout << "股票 3 买入" << endl;
40 }
41 };
42
43 class Stock4
44 {
45 public:
46 void Sell()
47 {
48 cout << "股票 4 卖出" << endl;
49 }
50 void Buy()
51 {
52 cout << "股票 4 买入" << endl;
53 }
54 };
55
56 class Fund
57 {
58 private:
59 Stock1* s1;
60 Stock2* s2;
61 Stock3* s3;
62 Stock4* s4;
63 public:
64 Fund() : s1(new Stock1), s2(new Stock2), s3(new Stock3), s4(new Stock4) {}
65 ~Fund()
66 {
67 delete s1;
68 delete s2;
69 delete s3;
70 delete s4;
71 }
72 void Sell()
73 {
74 s1->Sell();
75 s2->Sell();
76 s3->Sell();
77 s4->Sell();
78 }
79 void Buy()
80 {
81 s1->Buy();
82 s2->Buy();
83 s3->Buy();
84 s4->Buy();
85 }
86 };
87
88 int main()
89 {
90 Fund f;
91 f.Buy();
92 f.Sell();
93 return 0;
94 }
posted @
2011-04-26 15:49 unixfy 阅读(252) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
函数实现将网址进行如下操作
www.google.com 转成 com.google.www 及 mail.netease.com 转成 com.netease.mail
不允许用STL,空间为 O(1)
http://topic.csdn.net/u/20110425/12/8b5e155c-73d1-40af-84b8-6b6493f638e2.html一开始把 O(1) 看做时间复杂度了,如果是空间复杂度,直接在原地两次翻转即可。整体翻转,部分翻转顺序可以任意。
1 #include <iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 void reverse_(char* s, int left, int right)
5 {
6 while (left < right)
7 {
8 s[left] ^= s[right];
9 s[right] ^= s[left];
10 s[left] ^= s[right];
11 ++left;
12 --right;
13 }
14 }
15
16 int findch(char* s, char c, int n)
17 {
18 int ret, len = strlen(s);
19 for (ret = n; ret < len; ++ret)
20 {
21 if (s[ret] == c)
22 {
23 return ret;
24 }
25 }
26 return -1;
27 }
28
29 char* reverse(char* s)
30 {
31 reverse_(s, 0, strlen(s) - 1);
32 int left = 0, right = findch(s, '.', left);
33 while (right != -1)
34 {
35 reverse_(s, left, right - 1);
36 left = right + 1;
37 right = findch(s, '.', left);
38 }
39 reverse_(s, left, strlen(s) - 1);
40 return s;
41 }
42
43 int main()
44 {
45 char s[100];
46 while (cin >> s)
47 {
48 cout << reverse(s) << endl;
49 }
50 return 0;
51 }
如果是时间复杂度呢?
这里由个限制,就是只有两个 . 符号时才成立。使用字符串数组存储字符串,将首尾字符串指针交换即可。
例如 mail.netease.com
存在于字符串指针数组中:
mail
.
netease
.
com
将指向 mail 和 指向 com 的两个字符串指针交换即可。
1 #include <iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 int main()
5 {
6 char* s[100];
7 int i;
8 for (i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
9 {
10 s[i] = new char[100];
11 }
12 char c;
13 i = 0;
14 int j = 0;
15 // while (cin >> c)
16 // while (scanf("%c", &c))
17 while (c = getchar())
18 {
19 if (c == '\n')
20 {
21 break;
22 }
23 if (c != '.')
24 {
25 s[i][j] = c;
26 ++j;
27 s[i][j] = '\0';
28 }
29 else
30 {
31 // s[i][j] = '\0';
32 ++i;
33 s[i][0] = c;
34 s[i][1] = '\0';
35 j = 0;
36 ++i;
37 }
38 }
39 char* t = s[0];
40 s[0] = s[i];
41 s[i] = t;
42 for (j = 0; j <= i; ++j)
43 {
44 cout << s[j];
45 }
46 cout << endl;
47 return 0;
48 }
posted @
2011-04-25 23:18 unixfy 阅读(257) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
来自于《大话设计模式》
模板方法模式:定义一个操作中的算法的骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。模板方法使得子类可以不改变一个算法的结构即可重定义该算法的某些特定步骤。
尽量将公共操作上移到基类中,这样便于修改,代码复用性更强。
UML 类图:
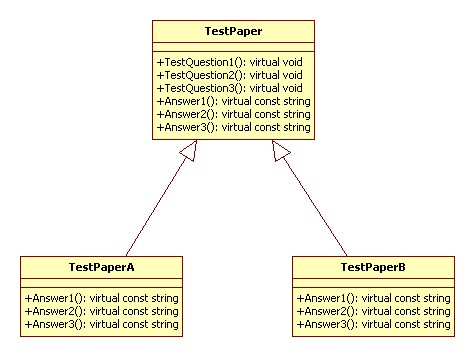
代码实现 C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string>
3 using namespace std;
4
5 class TestPaper
6 {
7 public:
8 virtual void TestQuestion1()
9 {
10 cout << "TestQuestion1" << endl;
11 cout << "Answer: " << Answer1() << endl;
12 }
13 virtual void TestQuestion2()
14 {
15 cout << "TestQuestion2" << endl;
16 cout << "Answer: " << Answer2() << endl;
17 }
18 virtual void TestQuestion3()
19 {
20 cout << "TestQuestion3" << endl;
21 cout << "answer: " << Answer3() << endl;
22 }
23 virtual const string Answer1() = 0
24 {
25 return "";
26 }
27 virtual const string Answer2() = 0
28 {
29 return "";
30 }
31 virtual const string Answer3() = 0
32 {
33 return "";
34 }
35 };
36
37 class TestPaperA : public TestPaper
38 {
39 public:
40 virtual const string Answer1()
41 {
42 return "a";
43 }
44 virtual const string Answer2()
45 {
46 return "b";
47 }
48 virtual const string Answer3()
49 {
50 return "c";
51 }
52 };
53
54 class TestPaperB : public TestPaper
55 {
56 public:
57 virtual const string Answer1()
58 {
59 return "c";
60 }
61 virtual const string Answer2()
62 {
63 return "b";
64 }
65 virtual const string Answer3()
66 {
67 return "a";
68 }
69 };
70
71 int main()
72 {
73 TestPaperA a;
74 a.TestQuestion1();
75 a.TestQuestion2();
76 a.TestQuestion3();
77
78 TestPaperB b;
79 b.TestQuestion1();
80 b.TestQuestion2();
81 b.TestQuestion3();
82
83 TestPaper* p;
84 p = new TestPaperA;
85 p->TestQuestion1();
86 p->TestQuestion2();
87 p->TestQuestion3();
88 delete p;
89
90 p = new TestPaperB;
91 p->TestQuestion1();
92 p->TestQuestion2();
93 p->TestQuestion3();
94 delete p;
95
96 return 0;
97 }
posted @
2011-04-25 16:41 unixfy 阅读(181) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
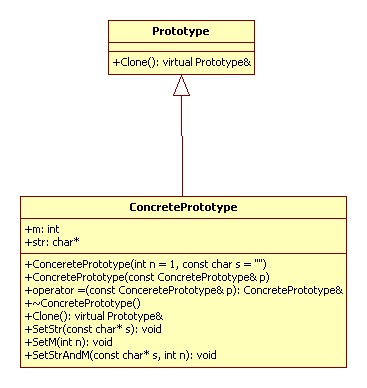
来自于《大话设计模式》
原型模式(Prototype):用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象。
这个设计模式在 C++ 中如何实现?
UML 图:
代码实现 C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 class Prototype
5 {
6 public:
7 virtual Prototype& Clone() = 0;
8 };
9
10 class ConcretePrototype
11 {
12 private:
13 int m;
14 char* str;
15 public:
16 ConcretePrototype(int n = 0, const char* s = "") : m(n)
17 {
18 str = new char[strlen(s) + 1];
19 if (str == 0)
20 {
21 exit(1);
22 }
23 strcpy(str, s);
24 }
25 ConcretePrototype(const ConcretePrototype& p)
26 {
27 str = new char[strlen(p.str) + 1];
28 if (str == 0)
29 {
30 exit(1);
31 }
32 strcpy(str, p.str);
33 m = p.m;
34 }
35 ConcretePrototype& operator =(const ConcretePrototype& p)
36 {
37 if (this == &p)
38 {
39 delete [] str;
40 str = new char[strlen(p.str) + 1];
41 if (str == 0)
42 {
43 exit(1);
44 }
45 strcpy(str, p.str);
46 m = p.m;
47 }
48 return *this;
49 }
50 ~ConcretePrototype()
51 {
52 delete [] str;
53 }
54 ConcretePrototype& Clone()
55 {
56 return *this;
57 }
58 void SetStr(const char* s = "")
59 {
60 delete [] str;
61 str = new char[strlen(s) + 1];
62 if (str == 0)
63 {
64 exit(1);
65 }
66 strcpy(str, s);
67 }
68 void SetM(int n)
69 {
70 m = n;
71 }
72 void SetStrAndM(const char* s, int n)
73 {
74 delete [] str;
75 str = new char[strlen(s) + 1];
76 if (str == 0)
77 {
78 exit(1);
79 }
80 strcpy(str, s);
81 m = n;
82 }
83 void test()
84 {
85 cout << m << endl;
86 cout << str << endl;
87 }
88 };
89
90 int main()
91 {
92 ConcretePrototype c(5, "abc");
93 c.test();
94
95 ConcretePrototype c2 = static_cast<ConcretePrototype>(c.Clone());
96 c2.test();
97
98 c2.SetStrAndM("xyz", 7);
99 c2.test();
100
101 return 0;
102
103 }
posted @
2011-04-25 16:03 unixfy 阅读(316) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏来自于《大话设计模式》
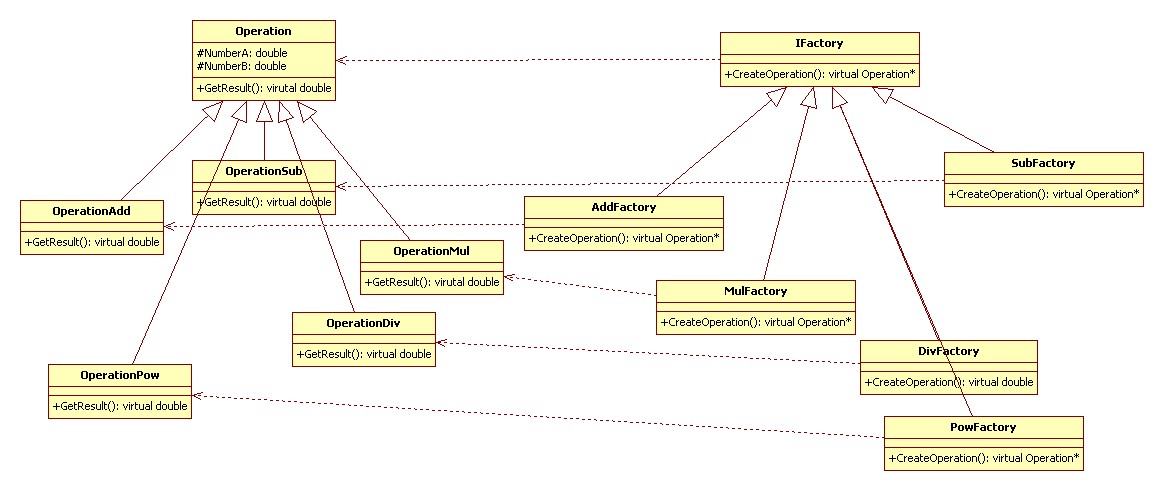
工厂方法模式(Factory Method):定义一个用于创建对象的接口,让子类决定实例化哪一个类。工厂方法使一个类的实例化延迟到其子类。
有一个操作类 Operation,继承其而派生出具体各个操作的操作派生类。
产生操作类的工厂基类 IFactory,继承其而派生出产生具体操作类的工厂派生类。
UML 类图:
代码实现 C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <cmath>
3 using namespace std;
4
5 class Operation
6 {
7 protected:
8 double NumberA;
9 double NumberB;
10 public:
11 virtual void SetNumberA(double a)
12 {
13 NumberA = a;
14 }
15 virtual void SetNumberB(double b)
16 {
17 NumberB = b;
18 }
19 virtual double GetResult() = 0;
20 };
21
22 class OperationAdd : public Operation
23 {
24 public:
25 virtual double GetResult()
26 {
27 return NumberA + NumberB;
28 }
29 };
30
31 class OperationSub : public Operation
32 {
33 public:
34 virtual double GetResult()
35 {
36 return NumberA - NumberB;
37 }
38 };
39
40 class OperationMul : public Operation
41 {
42 public:
43 virtual double GetResult()
44 {
45 return NumberA * NumberB;
46 }
47 };
48
49 class OperationDiv : public Operation
50 {
51 public:
52 virtual double GetResult()
53 {
54 if (NumberB == 0)
55 {
56 throw runtime_error("NumberB = 0!");
57 }
58 return NumberA / NumberB;
59 }
60 };
61
62 class OperationPow : public Operation
63 {
64 public:
65 virtual double GetResult()
66 {
67 if (NumberA == 0 && NumberB <= 0)
68 {
69 throw runtime_error("NumberA = 0, NumberB <= 0!");
70 }
71 return pow(NumberA, NumberB);
72 }
73 };
74
75 class IFactory
76 {
77 public:
78 virtual Operation* CreateOperation() = 0;
79 };
80
81 class AddFactory : public IFactory
82 {
83 public:
84 virtual Operation* CreateOperation()
85 {
86 return new OperationAdd;
87 }
88 };
89
90 class SubFactory : public IFactory
91 {
92 public:
93 virtual Operation* CreateOperation()
94 {
95 return new OperationSub;
96 }
97 };
98
99 class MulFactory : public IFactory
100 {
101 public:
102 virtual Operation* CreateOperation()
103 {
104 return new OperationMul;
105 }
106 };
107
108 class DivFactory : public IFactory
109 {
110 public:
111 virtual Operation* CreateOperation()
112 {
113 return new OperationDiv;
114 }
115 };
116
117 class PowFactory : public IFactory
118 {
119 public:
120 virtual Operation* CreateOperation()
121 {
122 return new OperationPow;
123 }
124 };
125
126 int main()
127 {
128 double a, b;
129 while (cin >> a >> b)
130 {
131 IFactory* pfactory = new AddFactory;
132 Operation* poperation = pfactory->CreateOperation();
133 poperation->SetNumberA(a);
134 poperation->SetNumberB(b);
135 cout << poperation->GetResult() << endl;
136 delete pfactory;
137 delete poperation;
138
139 pfactory = new SubFactory;
140 poperation = pfactory->CreateOperation();
141 poperation->SetNumberA(a);
142 poperation->SetNumberB(b);
143 cout << poperation->GetResult() << endl;
144 delete pfactory;
145 delete poperation;
146
147 pfactory = new MulFactory;
148 poperation = pfactory->CreateOperation();
149 poperation->SetNumberA(a);
150 poperation->SetNumberB(b);
151 cout << poperation->GetResult() << endl;
152 delete pfactory;
153 delete poperation;
154
155 pfactory = new DivFactory;
156 poperation = pfactory->CreateOperation();
157 poperation->SetNumberA(a);
158 poperation->SetNumberB(b);
159 try
160 {
161 cout << poperation->GetResult() << endl;
162 }
163 catch (const runtime_error& e)
164 {
165 cerr << e.what() << endl;
166 }
167 delete pfactory;
168 delete poperation;
169
170 pfactory = new PowFactory;
171 poperation = pfactory->CreateOperation();
172 poperation->SetNumberA(a);
173 poperation->SetNumberB(b);
174 cout << poperation->GetResult() << endl;
175 delete pfactory;
176 delete poperation;
177 }
178 }
posted @
2011-04-25 15:30 unixfy 阅读(229) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏